Clinical validation of quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen assays to estimate SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in nasopharyngeal swabs
- PMID: 33423918
- PMCID: PMC7713570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.11.021
Clinical validation of quantitative SARS-CoV-2 antigen assays to estimate SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in nasopharyngeal swabs
Abstract
Background: Expansion of the testing capacity for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is an important issue to mitigate the pandemic of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) caused by this virus. Recently, a sensitive quantitative antigen test (SQT), Lumipulse® SARS-CoV-2 Ag, was developed. It is a fully automated chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay system for SARS-CoV-2.
Methods: In this study, the analytical performance of SQT was examined using clinical specimens from nasopharyngeal swabs using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) as a control.
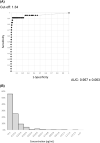
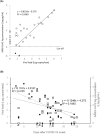
Results: Receiver operating characteristic analysis of 24 SARS-CoV-2-positive and 524 -negative patients showed an area under the curve of 0.957 ± 0.063. Using a cut-off value of 1.34 pg/ml, the sensitivity was 91.7%, the specificity was 98.5%, and the overall rate of agreement was 98.2%. In the distribution of negative cases, the 99.5 percentile value was 1.03 pg/ml. There was a high correlation between the viral load calculated using the cycle threshold value of RT-PCR and the concentration of antigen. The tendency for the antigen concentration to decrease with time after disease onset correlated with that of the viral load.
Conclusions: Presented results indicate that SQT is highly concordant with RT-PCR and should be useful for the diagnosis of COVID-19 in any clinical setting. Therefore, this fully automated kit will contribute to the expansion of the testing capability for SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay; Covid-19; Nasopharyngeal swab; Nasopharynx; SARS-CoV-2; Saliva; Sensitive quantitative antigen test.
Copyright © 2020 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest SYa and SO are employees of Fujirebio, Inc. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---... Accessed 4 December 2020.
-
- Yamakawa K., Fujimoto Y., Miyamoto K., Oshima T., Suzuki T., Nagata N., et al. Development of a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection reagent using immunochromatography. Jpn J Med Pharm Sci. 2020;77(6):937–944.
-
- Omi K., Takeda Y., Mori M. SARS-CoV-2 qRT-PCR Ct value distribution in Japan and possible utility of rapid antigen testing kit. medRxiv. 2020 June 19 doi: 10.1101/2020.06.16.20131243. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

