Spinopelvic alignment does not change after bilateral total hip arthroplasty in patients with bilateral Crowe type-IV developmental dysplasia of the hip
- PMID: 33423988
- PMCID: PMC7815221
- DOI: 10.5152/j.aott.2020.19043
Spinopelvic alignment does not change after bilateral total hip arthroplasty in patients with bilateral Crowe type-IV developmental dysplasia of the hip
Abstract
Objective: This prospective study aimed to evaluate the changes in the sagittal alignment after total hip arthroplasty (THA) in patients with hip osteoarthritis (OA) secondary to Crowe type-IV developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) and whether THA would contribute to the relief of low-back pain (LBP).
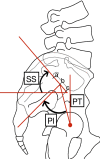
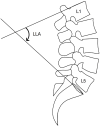
Methods: A total of 27 patients (2 men and 25 women) with bilateral hip OA secondary to Crowe type-IV DDH were enrolled in this study. Their mean age at the time of surgery was 40,36±12,35. All patients underwent simultaneous, bilateral THA between January 2015 and December 2016. Clinical assessment included Oswestry disability index (ODI) score and Harris hip score (HHS), and pelvic incidence (PI), sacral slope (SS), lumbar lordosis (LL), and pelvic tilt (PT) were measured from radiographs.
Results: Preoperatively, all the patients had hip and low-back pain. Preoperative and final follow-up ODI scores were 48.3 and 3.9 (p=0.000), respectively. HHS changed from 43.54 to 92.68 (p=0.000). PT and PI significantly changed from -20.4°±20.4° to 3.2°±16.7° (p=0.001) and from 26.6°±35.1° to 47.4°±17.9° (p=0.001), respectively. There were no significant differences regarding the SS and LL measurements. Age or limb-length discrepancy was not significantly associated with the spinopelvic alignment measurements.
Conclusion: Restoring the function of the hip with THA is shown to improve hip-associated LBP, but the accompanying hyperlordosis does not change. THA in patients with bilateral Crowe type-IV hips relieves hip pain as well as associated LBP. Hyperlordosis of the lumbar vertebra does not change after surgery, but PI and PT changes are observed; this improvement might have a role in the relief of LBP.
Level of evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on ''Spinopelvic alignment does not change after bilateral total hip arthroplasty in patients with bilateral Crowe type-IV developmental dysplasia of the hip'' by Can et al.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021 Aug;55(4):367-368. doi: 10.5152/j.aott.2021.21044. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021. PMID: 34464315 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
