Short-term outcomes of percutaneous pedicle screw fixation combined with vertebroplasty: A minimally invasive treatment for Kümmell's disease with intravertebral instability
- PMID: 33423997
- PMCID: PMC7815225
- DOI: 10.5152/j.aott.2020.19245
Short-term outcomes of percutaneous pedicle screw fixation combined with vertebroplasty: A minimally invasive treatment for Kümmell's disease with intravertebral instability
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to present early clinical and radiological outcomes of percutaneous pedicle screw fixation (PPSF) combined with vertebroplasty (VP) in the treatment of Kümmell's disease with intravertebral instability.
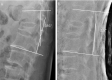
Methods: In this study, 21 consecutive patients (4 male and 17 female; mean age = 75.6 years; age range=65-86 years) who suffered from stage II and III Kümmell's disease with intravertebral instability were prospectively recruited from 2012 to 2016 and treated with PPSF combined with VP. The Cobb angle (CA) or wedge angle (WA) in both flexion and extension positions was measured using lateral radiographs, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging. In addition to these radiological parameters, clinical outcome measures, including the visual analog scale (VAS) and the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) were collected preoperatively; 1 week and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively; and then annually. Complications were also recorded.
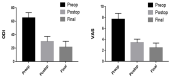
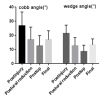
Results: The mean follow-up was 19.3 (range=12-36) months. The mean operating time was 135.4 (range, 110-175) min, and the mean estimated blood loss was 106.9 (range, 50-165) mL. The mean VAS score and ODI significantly decreased from 7.7±1.1 and 65.3%±7.7% preoperatively to 3.4±0.6 and 30.0%±7.6% postoperatively, respectively (p<0.05). At the final follow-up, the mean VAS score and ODI were 2.5±0.8 and 21.5%±8.8%, respectively (p>0.05). CA and WA significantly decreased from 26.9°±9.7° and 21.3°±6.0° preoperatively to 12.7°±7.2° to 8.6°±4.5° postoperatively, respectively (p<0.05). At the final follow-up, CA was 4.2°±2.0°, and WA was 4.7°±1.8° (p>0.05). No major complications were encountered during the follow-up period.
Conclusion: PPSF combined with VP seems to be an effective surgical option for the treatment of Kümmell's disease with intravertebral instability.
Level of evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ultrasonography-guided canal decompression combined with vertebroplasty and cement-augmented pedicle screw fixation for stage III Kümmell's disease with neurological deficits: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 12;25(1):805. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07929-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39395951 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell's Disease.Pain Physician. 2015 Jul-Aug;18(4):373-81. Pain Physician. 2015. PMID: 26218941
-
A comparative study of PSPVP and PSIBG in the treatment of stage II-III Kummell's disease.Biomed Mater Eng. 2023;34(3):261-276. doi: 10.3233/BME-221456. Biomed Mater Eng. 2023. PMID: 36213986
-
Vertebral augmentation plus short-segment fixation versus vertebral augmentation alone in Kümmell's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2022 Apr;45(2):1009-1018. doi: 10.1007/s10143-021-01661-8. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Neurosurg Rev. 2022. PMID: 34596773
-
Efficacy and safety of vertebroplasty versus posterior pedicle screw in treating stage III Kummell's disease without neurological deficits: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. 2025 Jul;53(7):3000605251353732. doi: 10.1177/03000605251353732. Epub 2025 Jul 4. J Int Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40613656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The surgical strategy selection and clinical efficacy analysis of Kummell's disease.Eur Spine J. 2024 Dec;33(12):4488-4498. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08469-2. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 39343794
-
Ultrasonography-guided canal decompression combined with vertebroplasty and cement-augmented pedicle screw fixation for stage III Kümmell's disease with neurological deficits: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 12;25(1):805. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07929-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39395951 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Cements Used in Vertebral Augmentation: A State-of-the-art Narrative Review.J Pain Res. 2024 Mar 13;17:1029-1040. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S437827. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38505504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Percutaneous Transpedicular Intravertebral Cage Augmentation with Short-Segment Fixation Using Specially Designed Cannulated Cage Trials for Advanced Kümmell Disease: A Preliminary Study Comparing with Vertebroplasty with Short-Segment Fixation.Clin Orthop Surg. 2025 Feb;17(1):29-38. doi: 10.4055/cios24276. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Clin Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 39912073 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous short segmental fixation combined with bone cement augmentation for stage III Kümmell's disease without nerve deformity.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jan 26;103(4):e37087. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037087. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38277523 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
