Discovery of New Fusion Inhibitor Peptides against SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting the Spike S2 Subunit
- PMID: 33424013
- PMCID: PMC8094075
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.201
Discovery of New Fusion Inhibitor Peptides against SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting the Spike S2 Subunit
Abstract
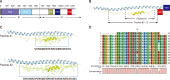
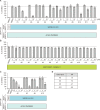
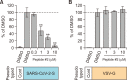
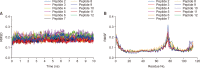
A novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), caused a worldwide pandemic. Our aim in this study is to produce new fusion inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2, which can be the basis for developing new antiviral drugs. The fusion core comprising the heptad repeat domains (HR1 and HR2) of SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) were used to design the peptides. A total of twelve peptides were generated, comprising a short or truncated 24-mer (peptide #1), a long 36-mer peptide (peptide #2), and ten peptide #2 analogs. In contrast to SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 S-mediated cell-cell fusion cannot be inhibited with a minimal length, 24-mer peptide. Peptide #2 demonstrated potent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 S-mediated cell-cell fusion at 1 µM concentration. Three peptide #2 analogs showed IC50 values in the low micromolar range (4.7-9.8 µM). Peptide #2 inhibited the SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus assay at IC50=1.49 µM. Given their potent inhibition of viral activity and safety and lack of cytotoxicity, these peptides provide an attractive avenue for the development of new prophylactic and therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Antiviral drugs; COVID-19; Fusion inhibitors; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bashyal S., Noh G., Keum T., Choi Y. W., Lee S. Cell penetrating peptides as an innovative approach for drug delivery; then, present and the future. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016;46:205–220. doi: 10.1007/s40005-016-0253-0. - DOI
-
- Chu L. H. M., Chan S. H., Tsai S. N., Wang Y., Cheng C. H. K., Wong K. B., Waye M. M. Y., Ngai S. M. Fusion core structure of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV): in search of potent SARS-CoV entry inhibitors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008;104:2335–2347. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21790. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

