Predicting mid-life capital formation with pre-school delay of gratification and life-course measures of self-regulation
- PMID: 33424063
- PMCID: PMC7792663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jebo.2019.08.016
Predicting mid-life capital formation with pre-school delay of gratification and life-course measures of self-regulation
Abstract
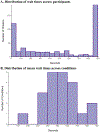
How well do pre-school delay of gratification and life-course measures of self-regulation predict mid-life capital formation? We surveyed 113 participants of the 1967-1973 Bing pre-school studies on delay of gratification when they were in their late 40's. They reported 11 mid-life capital formation outcomes, including net worth, permanent income, absence of high-interest debt, forward-looking behaviors, and educational attainment. To address multiple hypothesis testing and our small sample, we pre-registered an analysis plan of well-powered tests. As predicted, a newly constructed and pre-registered measure derived from preschool delay of gratification does not predict the 11 capital formation variables (i.e., the sign-adjusted average correlation was 0.02). A pre-registered composite self-regulation index, combining preschool delay of gratification with survey measures of self-regulation collected at ages 17, 27, and 37, does predict 10 of the 11 capital formation variables in the expected direction, with an average correlation of 0.19. The inclusion of the preschool delay of gratification measure in this composite index does not affect the index's predictive power. We tested several hypothesized reasons that preschool delay of gratification does not have predictive power for our mid-life capital formation variables.
Keywords: D140; D910; Delay of gratification; I120; I210; I310; Mid-life capital formation; Self-regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ayduk Ö, et al. , 2000. Regulating the interpersonal self: strategic self-regulation for coping with rejection sensitivity. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol 79, 776–792. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A, Mischel W, 1965. Modifications of self-imposed delay of reward through exposure to live and symbolic models. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol 2 (5), 698–705. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y, 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 57, 289–300.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
