Postoperative Pain Scores After Open Inguinal Hernia Repair: Comparison of Three Postoperative Analgesic Regimens
- PMID: 33424089
- PMCID: PMC7780791
- DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2020.74.355-358
Postoperative Pain Scores After Open Inguinal Hernia Repair: Comparison of Three Postoperative Analgesic Regimens
Abstract
Introduction: Pain management after open inguinal hernia repair has become an issue that physicians deal with on a daily basis.
Aim: The purpose of this study was to investigate the analgesic effect of three different regimens of analgesics administered to patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair.
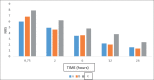
Methods: A total of 259 patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair were enrolled. Patients were randomly allocated to one of three groups on admission, which would determine the prescribed post-operative analgesic regimen. Patients allocated to group A receiving a combination of 1gr/8hours intravenous (IV) acetaminophen and 50mg/6hours intramuscular (IM) pethidine, patients in group B receiving a combination of 1gr/8hours IV acetaminophen and 40mg/12hours IV parecoxib, while patients of group C received 1gr/8hours IV acetaminophen monotherapy. All patients remained overnight at the hospital and discharged the day after. Analgesic therapy was administered at regular intervals. Pain was evaluated utilizing the numeric rating scale (NRS) at 5 time points: the first assessment was done at 45 minutes, the second at 2 hours, the third at 6 hours, the fourth at 12 hours and the fifth at 24 hours post-administration. The postoperative pain intensities measured by NRS within groups and between groups at each time were analyzed using one-way repeat measured ANOVA and Post Hoc Test-Bonferroni Correlation.
Results: The analgesic regimens of groups A and B (combination regimens consisting of IV acetaminophen and intramuscular pethidine and IV acetaminophen and IV parecoxib, respectively) were found to be of equivalent efficacy (P-value=1.000). In contrast, patients in group C (acetaminophen monotherapy) had higher NRS scores, compared to both patients in groups A (P-value<0.0001) and B (P-value<0.0001).
Conclusion: The combinations of IV acetaminophen with either intramuscular pethidine or IV parecoxib are superior to IV acetaminophen monotherapy in achieving pain control in patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair.
Keywords: inguinal hernia repair; numerical rating score; pain score; postoperative analgesia; postoperative pain.
© 2020 Francesk Mulita, Nikolaos Parchas, Konstantina Solou, Levan Tchabashvili, Foteini Gatomati, Fotios Iliopoulos, Ioannis Maroulis.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Read RC. Herniology: past, present, and future. Hernia. 2009 Dec;13(6):577–80. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgibbons RJ, Ramanan B, Arya S, et al. Long-term results of a randomized controlled trial of a nonoperative strategy (watchful waiting) for men with minimally symptomatic inguinal hernias. Ann Surg. 2013;258:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Bachul P, Tomaszewski KA, Kmiotek EK, Kratochwil M, Solecki R, Walocha JA. Anatomic variability of groin innervation. Folia Morphol. (Warsz) 2013 Aug;72(3):267–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical