The application of exogenous PopW increases the tolerance of Solanum lycopersicum L. to drought stress through multiple mechanisms
- PMID: 33424162
- PMCID: PMC7772130
- DOI: 10.1007/s12298-020-00918-8
The application of exogenous PopW increases the tolerance of Solanum lycopersicum L. to drought stress through multiple mechanisms
Abstract
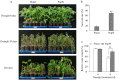
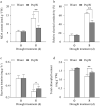
Tomato is a major cultivated vegetable species of great economic importance throughout the world, but its fruit yield is severely impaired by drought stress. PopW, a harpin protein from Ralstonia solanacearum ZJ3721, plays vital roles in various plant defence responses and growth. In this study, we observed that the foliar application of PopW increased tomato drought tolerance. Our results showed that compared with water-treated plants, PopW-treated plants presented a significantly higher recovery rate and leaf relative water content under drought-stress conditions. PopW decreased the malondialdehyde content and relative electrical conductivity by 40.2% and 21%, respectively. Drought disrupts redox homeostasis through the excessive accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). PopW-treated plants displayed an obvious reduction in ROS accumulation due to enhanced activities of the antioxidant enzyme catalase, superoxide dismutase and peroxidase. Moreover, PopW promoted early stomatal closure, thereby minimizing the water loss rate of plants under drought stress. Further investigation revealed that endogenous abscisic acid (ABA) levels and the transcript levels of drought-responsive genes involved in ABA signal transduction pathways increased in response to PopW. These results confirm that PopW increases drought tolerance through multiple mechanisms involving an enhanced water-retention capacity, balanced redox homeostasis, increased osmotic adjustment, reduced membrane damage and decreased stomatal aperture, suggesting that the application of exogenous PopW may be a potential method to enhance tomato drought tolerance.
Keywords: Drought tolerance; Osmotic adjustment; PopW; Redox homeostasis; Solanum lycopersicum L; Stomatal closure.
© Springer Nature India Private Limited part of Springer Nature 2020.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Overexpression of a harpin-encoding gene popW from Ralstonia solanacearum primed antioxidant defenses with enhanced drought tolerance in tobacco plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2016 Jun;35(6):1333-44. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-1965-3. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Plant Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27053225
-
PopW enhances drought stress tolerance of alfalfa via activating antioxidative enzymes, endogenous hormones, drought related genes and inhibiting senescence genes.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Sep;166:540-548. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.06.036. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34174659
-
Exogenous Abscisic Acid Priming Modulates Water Relation Responses of Two Tomato Genotypes With Contrasting Endogenous Abscisic Acid Levels to Progressive Soil Drying Under Elevated CO2.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Nov 24;12:733658. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.733658. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34899772 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Stomatal Closure in Plants Exposed to Drought and Cold Stress.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1081:215-232. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1244-1_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30288712 Review.
-
Biotechnological Interventions in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) for Drought Stress Tolerance: Achievements and Future Prospects.BioTech (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;11(4):48. doi: 10.3390/biotech11040048. BioTech (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36278560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics, Roles and Applications of Proteinaceous Elicitors from Pathogens in Plant Immunity.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;13(2):268. doi: 10.3390/life13020268. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving crop drought resistance with plant growth regulators and rhizobacteria: Mechanisms, applications, and perspectives.Plant Commun. 2021 Aug 4;3(1):100228. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2021.100228. eCollection 2022 Jan 10. Plant Commun. 2021. PMID: 35059626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in physio-biochemical metabolism, phenolics and antioxidant capacity during germination of different wheat varieties.Food Chem X. 2024 May 1;22:101429. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101429. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38756466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashraf M, Iram A. Drought stress induced changes in some organic substances in nodules and other plant parts of two potential legumes differing in salt tolerance. Flora. 2005;200:535–546. doi: 10.1016/j.flora.2005.06.005. - DOI
-
- Barrs HD, Weatherley PE. A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficits in leaves. A J Biol Sci. 1962;15:413–428. doi: 10.1071/BI9620413. - DOI
-
- Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil. 1973;39:205–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00018060. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
