Options and limitations of implant constraint
- PMID: 33424186
- PMCID: PMC7779836
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.12.013
Options and limitations of implant constraint
Abstract
With an ever-increasing number of revisions, the surgeons will be faced with the dilemma of choosing the right implant for the revision knee. The soft tissue viability governs the choice of an implant at the time of revision. The selection ranges from the cruciate-retaining to the rotating/fixed hinge implants. The surgeon needs to plan preoperatively, but usually, the final decisions are made intraoperative. As determining the amount of constraint necessary can be challenging, we have tried to lay down a few pointers, which would help to make that choice. The posterior stabilized implants can manage most revision knees; in certain situations where they cannot accommodate the flexion-extension gap imbalance, a varus-valgus constrained implant should be used. The rotating hinge implants are used for severe instabilities or loss of soft tissue or bone around the knee. The use of a higher constraint implant has its consequences like reduced life span and reduced function. Thus it is crucial to use the least amount of constraint as necessary - however, as much as required.
Keywords: Constraint; Revision knee; Revision total knee arthroplasty; Rotating hinge; Stems; Varus valgus constrained.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation.
Figures


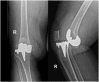
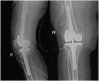

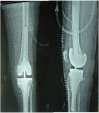

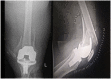



References
-
- Babis G.C., Trousdale R.T., Morrey B.F. The effectiveness of isolated tibial insert exchange in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(1):64. - PubMed
-
- Jo A.R., Song E.K., Lee K.B., Seo H.Y., Kim S.K., Seon J.K. A comparison of stability and clinical outcomes in single-radius versus multi-radius femoral design for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29:2402–2406. - PubMed
-
- Park C.H., Bae J.K., Song S.J. Factors affecting the choice of constrained prostheses when performing revision total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2019;43(8):1831–1840. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

