Targeted drug delivery of Methotrexate in situ gels for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 33424248
- PMCID: PMC7783075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.10.003
Targeted drug delivery of Methotrexate in situ gels for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
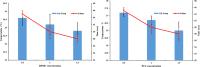
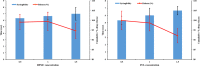
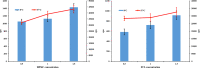
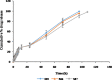
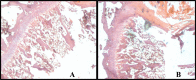
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is considered a debilitating disease that increases the risk of significant morbidity and premature mortality. To circumvent drug-related toxicity and ineffectiveness of anti-inflammatory drugs, there is a significant need for an advanced delivery system that increases bioavailability. The feasibility of in situ gel of methotrexate sodium (MTS) as an effective management for Rheumatoid arthritis was investigated. It was formulated with pluronic F-127 (PLF-127) as primary polymer, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose K4M (HK4M), and polycarbophil (PCL) as a copolymer and characterized by various parameters. The efficacy evaluation by Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA) model, biocompatibility assessment by histopathological studies conducted. The optimized in situ gel (M4) was thermoresponsive, released 93.26 ± 2.39% MTS at 96 hours. In addition, distribution of MTS was even in the optimized sterile and syringeable in situ gel. In vivo studies on wistar rats demonstrated a substantial reduction in paw oedema during the 28-day study period and were biocompatible with the tissues at the injection site. The study was successful in formulating, optimizing MTS in situ gel for effective management of RA.
Keywords: Drug targeting; In situ gel; Methotrexate sodium; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Abdel-Nasser A.M., Rasker J.J., Vaikenburg H.A. Epidemiological and clinical aspects relating to the variability of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis. Rheum. 1997;27:123–140. - PubMed
-
- Albert C., Brocq O., Gerard D., Roux C., Euller-Ziegler L. Septic knee arthritis after intra-articular hyaluronate injection. Joint. Bone. Spine. 2006;73:205–207. - PubMed
-
- Avina-Zubieta J.A., Choi H.K., Sadatsafavi M., Etminan M., Esdaile J.M., Lacaille D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis. Rheum. 2008;59:1690–1697. - PubMed
-
- Bozdag S., Dillen K., Vandervoort J., Ludwig A. The effect of freeze-drying with different cryoprotectants and gamma-irradiation sterilization on the characteristics of ciprofloxacin HCl-loaded poly(D, L-lactide-glycolide) nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005;57:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Butoescu N., Jordan O., Doelker E. Intra-articular drug delivery systems for the treatment of rheumatic diseases: A review of the factors influencing their performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009;73:205–218. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

