Application of quercetin flavonoid based hybrid nanocomposites: A review
- PMID: 33424263
- PMCID: PMC7783214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.10.017
Application of quercetin flavonoid based hybrid nanocomposites: A review
Abstract
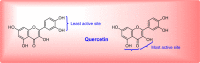
Natural bioflavonoids are an essential component of dietary supplements possessing antimicrobial properties. Many of the bioflavonoids have resulted in positive antitumor, anticancer, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory properties, but the efficacy remains low due to toxicity at the molecular level whereas antiviral property limits to negative. The synergistic link between nanoscience and flavonoid chemistry enhances the epidemiological properties of flavonoid and also diminish the antimicrobial resistivity (AMR) by forming their hybrid nanocomposites. Nanochemistry uses various nanocomposite and nanomaterials for biosensing the flavonoids and their delivery as a drug. The quercetin flavonoid and its derivatives such as rutin, and myricetin are used for sensing and drug delivery. Quercetin with 15Carbon-5Hydroxyl chemical scaffold has been explored for a few decades for the development of hybrid nanocomposite and nanomaterial with metallic as well as organic nano co-composites. This quercetin flavonoid based hybrid nanocomposites seemed to show a significant effect on In vitro and some animal model processes along with attenuating lipid peroxidation, platelet aggregation, and capillary permeability actions. This review mainly focused on the hybrid nanoscience of quercetin bioflavonoid and its application in numerous biological, material fields with a future perspective.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistivity; Biomedical applications; Flavonoid; Nanocomposites; Quercetin.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quercetin, the Potential Powerful Flavonoid for Human and Food: A Review.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2024 Sep 24;16(3):30. doi: 10.31083/j.fbe1603030. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2024. PMID: 39344383 Review.
-
Review of the biology of Quercetin and related bioflavonoids.Food Chem Toxicol. 1995 Dec;33(12):1061-80. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(95)00077-1. Food Chem Toxicol. 1995. PMID: 8847003 Review.
-
O-Glycoside quercetin derivatives: Biological activities, mechanisms of action, and structure-activity relationship for drug design, a review.Phytother Res. 2022 Feb;36(2):778-807. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7352. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 34964515 Review.
-
The flavonoid rutin and its aglycone quercetin modulate the microglia inflammatory profile improving antiglioma activity.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Mar;85:170-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 3. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 31059805
-
Quercetin nanocomposite as novel anticancer therapeutic: improved efficiency and reduced toxicity.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013 Jun 14;49(3):359-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013. PMID: 23602995
Cited by
-
Poly(vinyl chloride) Films Incorporated with Antioxidant ZnO-Flavonoid Nanoparticles: A Strategy for Food Preservation.Foods. 2024 Aug 29;13(17):2745. doi: 10.3390/foods13172745. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272509 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Phenolic Compounds as Modifiers for Epoxidized Natural Rubber/Silica Hybrids.Molecules. 2022 Mar 29;27(7):2214. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072214. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408613 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Inhalation Therapy for Pulmonary Diseases.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(11):882-896. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220803103039. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35927812
-
Rapid and Versatile Biosensing of Liposome Encapsulation Efficiency Using Electrical Conductivity Sensor.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 8;13(9):878. doi: 10.3390/bios13090878. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754112 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin nanoparticles as a therapeutic approach: pharmacological actions and potential applications in therapy.BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2024 Dec 19;105(4):377-393. doi: 10.5114/bta.2024.145258. eCollection 2024. BioTechnologia (Pozn). 2024. PMID: 39844873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abd Soheir N., El-Rahmanand Suhailah S.A.-J. Quercetin nanoparticles: preparation and characterization. Indian J. Drugs. 2014;2:96–103.
-
- Alonso-Salces R.M., Ndjoko K., Queiroz E.F., Ioset J.R., Hostettmann K., Berrueta L.A., Gallo B., Vicente F. On-line characterisation of apple polyphenols by liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectracometry and ultraviolet absorbance detection. J. Chromatogr. A. 2004;1046:89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.06.077. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

