Sex differences in pregabalin-seeking like behavior in a conditioned place preference paradigm
- PMID: 33424265
- PMCID: PMC7783229
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.11.001
Sex differences in pregabalin-seeking like behavior in a conditioned place preference paradigm
Abstract
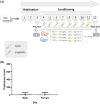
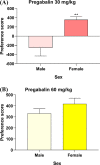
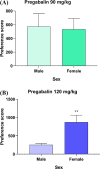
Substance abuse is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug use regardless of negative consequences. Incremental increases in pregabalin abuse have been observed in Saudi Arabia and throughout the world. In previous studies, the potential for pregabalin abuse with escalating doses of the drug (30, 60, 90, and 120 mg/kg) were investigated in male mice. Notably, researchers have argued that women may exhibit a greater tendency to consume drugs without a prescription to alleviate stress and depression. Moreover, female subjects are more prone to impulsivity in drug intake or abuse than their male counterparts. Therefore, in the present study, we compared the potential for pregabalin abuse between male and female mice using a conditioned place preference paradigm. Male and female BALB/c mice were divided into four groups based on the pregabalin dose administered (30, 60, 90, or 120 mg/kg, intraperitoneal). Preference scores were then calculated and compared between male and female mice in each dosage group. Interestingly, preference scores were significantly higher in female mice than in male mice at dosages of 30 and 120 mg/kg. These findings indicate that female mice may be more prone to pregabalin abuse and tolerance than male mice. These results might be helpful to the healthcare providers and policymakers to consider these sex differences in choosing therapeutic plans and consider alternatives to the misused prescription medications.
Keywords: Addiction; CPP, conditioned place preference; Conditioned place preference; Drug abuse; ER, estradiol receptor; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; Pregabalin; Sex differences; mGluR, metabotropic glutamate receptor.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar M.A., Rodríguez-Arias M., Miñarro J. Neurobiological mechanisms of the reinstatement of drug-conditioned place preference. Brain Res. Rev. 2009;59(2):253–277. - PubMed
-
- Al-Husseini A., Van Hout M.C., Wazaify M. Pregabalin misuse and abuse: a scoping review of extant literature. J. Drug Issues. 2018;48(3):356–376.
-
- Andrews N., Loomis S., Blake R., Ferrigan L., Singh L., McKnight A.T. Effect of gabapentin-like compounds on development and maintenance of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Psychopharmacology. 2001;157(4):381–387. - PubMed
-
- Back S.E., Brady K.T., Jackson J.L., Salstrom S., Zinzow H. Gender differences in stress reactivity among cocaine-dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology. 2005;180(1):169–176. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

