Pharmacological and computer-aided studies provide new insights into Millettia peguensis Ali (Fabaceae)
- PMID: 33424267
- PMCID: PMC7783235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.11.004
Pharmacological and computer-aided studies provide new insights into Millettia peguensis Ali (Fabaceae)
Abstract
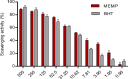
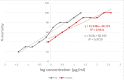
Millettia peguensis, popular for its ethnopharmacological uses, was employed to evaluate its different pharmacological properties in this study. The analgesic studies of the plant have been performed by acetic acid-induced writhing and formalin-induced licking tests respectively, whereas the antidiarrheal experiment was done by castor oil-induced diarrheal test. Besides, antioxidant, cytotoxic, antimicrobial, thrombolytic evaluations were performed by DPPH scavenging with phenol content determination, brine shrimp lethality, disc diffusion and clot lysis methods respectively. Moreover, in silico study of the phytoconstituents was carried out by molecular docking and ADME/T analysis. The methanol extract of Millettia peguensis (MEMP) revealed significant biological activity in the analgesic and antidiarrheal test (p < 0.001) compared to the standards. Antioxidant assay displayed promising IC50 values (15.96 μg/mL) with the total phenol content (65.27 ± 1.24 mg GAE/g). In the cytotoxicity study, the LC50 value was found to be 1.094 μg/mL. Besides, MEMP was highly sensitive to the bacteria but less liable to clot lysis. Furthermore, phytoconstituents exposed potential binding affinity towards the selected receptors, whereas the ADME/T properties indicated the drug likeliness of the plant. The outcomes of these findings suggest the therapeutic potential of this plant against pain, diarrhea, inflammation, and tissue toxicity.
Keywords: 5-HT3, 5-hydroxytryptamine 3; ASA, acetyl salicylic acid; Analgesic; Antidiarrheal; Antioxidant; Antitumor; BHT, butylated hydroxytoluene; CADD, computer-aided drug discovery; COX 1, cyclooxygenase-1; COX 2, cyclooxygenase-2; DPPH, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate; GABA, gamma-Aminobutyric acid; IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration; IL-1, interleukin-1; LC50, Lethal Concentration 50; MEMP, methanol extract of Millettia peguensis; MMP 9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; Millettia peguensis; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; RONS, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNF-alpha, tumour necrosis factor alpha.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Abdel Motaal N.A., Abdel Maguid A. Effect Of Fractionated And Single Doses Gamma Irradiation On Certain Mammalian Organs. Egypt. J. Hospital Med. 2005;19(1):111–122.
-
- Abe R., Ohtani K. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants and traditional therapies on Batan Island, the Philippines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013;145(2):554–565. - PubMed
-
- Abiy Y., Hellen A.O.R., Solomon J. Anti-plasmodial activities and X-ray crystal structures of rotenoids from Millettia usaramensis. Phytochemistry. 2003;64(3):773–779. - PubMed
-
- Agati G., Azzarello E., Pollastri S., Tattini M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: location and functional significance. Plant Sci. 2012;196:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Agbor G.A., Léopold T., Jeanne N.Y. The antidiarrhoeal activity of Alchornea cordifolia leaf extract. Phytotherapy Res.: Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Natural Product Derivatives. 2004;18(11):873–876. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

