Quantification of biochemical compounds in Bauhinia Variegata Linn flower extract and its hepatoprotective effect
- PMID: 33424304
- PMCID: PMC7785441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.09.056
Quantification of biochemical compounds in Bauhinia Variegata Linn flower extract and its hepatoprotective effect
Abstract
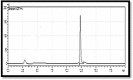
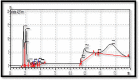
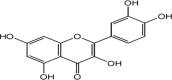
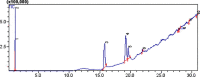
Liver disorders may occur as a result of exposure to chemical compounds capable of inducing the oxidative stress and hepatic injuries. The aim of present study was to investigate the effects of flower extracts of B. Variegata for the treatment of liver injury induced by the CCl4. About 1 ml/kg body weight (b.w) of CCl4 was induced to experimental mice by intraperitoneal way for 14 days. The methanol and chloroform extracts (100, 200 and 300 mg/kg b.w) were administered to experimental animals for 14 days along with standard drug Silymarine (100 mg/kg b.w). The extracts alone showed no evidence of hepatic toxicity but animals exposed to CCl4 without the treatment with B. Variegata presented variations in levels of liver enzymes, antioxidant enzymes, proteins and blood cells as well as injuries in liver cells were also observed during histopathological study. However, after the treatments especially with 300 mg/kg b.w of methanol flower extracts levels of liver markers (ALT, AST and ALP), antioxidant enzymes and blood cells decreases and turned towards normal levels. Whereas level of total proteins and bilirubin was improved and damaged liver cells were repaired. The curative activity of flower extracts can be correlated to the higher potential of antioxidants and occurrence of Quercetin and some other organic compounds those were investigated from flower extracts of B. Variegata during HPLC and GC-MS analysis. The finding of this study supports the use of B. Variegata flower formulation in folk medicines.
Keywords: Antioxidants; B. Variegata; HPLC; Hepatoprotective effect; Phytochemicals.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective properties of Bauhinia variegata bark extract.Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007 Sep;127(9):1503-7. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.127.1503. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17827931
-
Allium porrum and Bauhinia Variegata Mitigate Acute Liver Failure and Nephrotoxicity Induced by Thioacetamide in Male Rats.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2020 Apr;35(2):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s12291-018-0803-5. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32226246 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of methanolic extract of flowers of Nerium oleander against CCl4-induced liver injury in rats.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012 Sep;5(9):677-85. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(12)60106-0. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012. PMID: 22805717
-
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect of Bauhinia hookeri extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice and characterization of its bioactive compounds by HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS/MS.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:245171. doi: 10.1155/2014/245171. Epub 2014 May 14. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24955350 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective action of various partitions of methanol extract of Bauhinia purpurea leaves against paracetamol-induced liver toxicity: involvement of the antioxidant mechanisms.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jun 11;16:175. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1110-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27287196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Wild Edible Flowers of Indian Himalayan Region, Their Traditional Uses and Potential Health Benefits: A Way Forward for Food and Nutritional Security.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025 Feb 10;80(1):60. doi: 10.1007/s11130-025-01302-1. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39928195 Review.
-
Validation of an HPLC-DAD Method for Quercetin Quantification in Nanoparticles.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 17;16(12):1736. doi: 10.3390/ph16121736. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasi, A.M., M.H. Shah, T. Li, X. Fu, X. Guo and R.H. Liu. 2015. Ethnomedicinal values, phenolic contents and antioxidant properties of wild culinary vegetables. J. ethnopharmacol.,162(l):333-345. - PubMed
-
- AOAC. 2003. Official methods of analysis of the association of official’s analytical chemists, 17th edn. Association of official analytical chemists, Arlington, Virginia.
-
- Beeharry, N., J. E. Lowe, A. R. Hernandez, J. A. Chambers, F. Fucassi, P.J. Cragg, M. H. GreenandI.C. Green. 2003. Linoleic acid and antioxidants protect against DNA damage and apoptosis induced by palmitic acid. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis., 530(1-2): 27-33. - PubMed
-
- Bhuiyan M.N.I., Begum J., Bhuiyan M.N.H. Analysis of essential oil of eaglewood tree (Aquilaria agallocha Roxb.) by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Bang. J. Pharmacol. 2009;4(1):24–28.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

