Scenario of pathogenesis and socioeconomic burden of human brucellosis in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 33424306
- PMCID: PMC7783673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.09.059
Scenario of pathogenesis and socioeconomic burden of human brucellosis in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
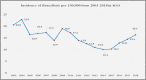
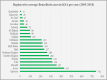
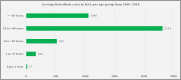
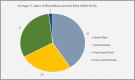
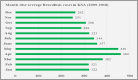
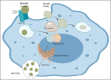
Brucellosis is considered a prevailing endemic infectious disease in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and represents a health problem with socio-economic burden. There are two main Brucella species that cause human brucellosis; Brucella abortus, and Brucella melitensis. The clinical features range from asymptomatic to the acute symptoms of fever, joint pain, muscle pain, headache, nausea/vomiting, anorexia and malaise in addition to the subsequent complications that might occur. The endemicity of brucellosis might be explained due to obstacles in controlling the importation of animals for slaughtering during Hajj periods and for several other predisposing factors. The distribution of the disease is all over the country and the most prevalent part is the south followed by north and then the east and central parts. However, in the complexity of brucellosis control measures, there are several activities which have been implemented to tackle the disease such as mass vaccination of animals, regulating importation of slaughter animals, and improving public awareness. This review provides a detailed description of the status of brucellosis in Saudi Arabia, which includes epidemiology, clinical characteristics, virulence and pathophysiology, and prevention of the disease.
Keywords: Brucellosis; Epidemiology; Prevalence; Saudi Arabia; Virulence.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Abedi A.-S. The prevalence of Brucella spp. in dairy products in the Middle East region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2020;202 105241. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Rabia, A., 2015. Indigenous medicine among the Bedouin in the Middle East. Berghahn Books.
-
- Al Dahouk S. Laboratory-based diagnosis of brucellosis–a review of the literature. Part I: Techniques for direct detection and identification of Brucella spp. Clin. Lab. 2003;49(9–10):487–505. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

