FbD directed fabrication and investigation of luliconazole based SLN gel for the amelioration of candidal vulvovaginitis: a 2 T (thermosensitive & transvaginal) approach
- PMID: 33424312
- PMCID: PMC7785458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.10.005
FbD directed fabrication and investigation of luliconazole based SLN gel for the amelioration of candidal vulvovaginitis: a 2 T (thermosensitive & transvaginal) approach
Abstract
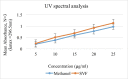
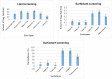
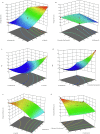
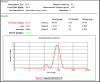
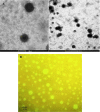
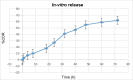
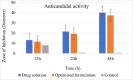
Candidal vulvovaginitis (CVV), is the second most leading vaginal infection (global prevalence > 75%), caused due to excessive growth of Candida spp., predominantly Candida albicans (>95% cases). The current treatment regimens for CVV are marred with the challenges of fungal resistance & infection recurrence, subsequently leading to the compromised therapeutic efficacy of anti-fungal drugs, prolonged treatment and low patient compliance. The core of the present research was the fabrication & investigation of 2 T-SLN (solid lipid nanoparticles) gel carrying luliconazole for the amelioration of CVV. '2T' symbolizes transvaginal & thermosensitive attributes of the present formulation. SLNs were prepared by a modified melt emulsification-ultra sonication method using a combination of solid lipids (Gelucire 50/13 & Precirol ATO 5), surfactant (Tween 80) and co-surfactant (Kolliphor). Formulation by design (FbD) approach was adopted to obtain appropriately screened and tailored SLNs. The optimized SLNs yielded a particle size, polydispersity index & entrapment efficiency of 62.18 nm, 0.263 & 81.5% respectively. To formulate the 2 T-gel, the final SLNs were loaded into Carbopol 971P-NF and Triethanolamine based gel. The 2 T-SLN gel was found to be easily spreadable and homogenous with mean extrudability (15 ± 0.4 g/cm2), viscosity (696.42 ± 2.34 Pa·s) and %drug content (93.24 ± 0.73%) values.. The pH of the prepared 2 T-SLN gel (4.5 ± 0.5) was in concordance with the vaginal pH (normal conditions). For in-vitro characterization of an optimized 2 T-SLN gel the release kinetics & anticandidal activity were assessed which offers a %cumulative drug release of 62 ± 0.5% in 72 h and 37.3 ± 1.5 mm zone of inhibition in 48 h. The visual appearance & dimensions were determined using fluorescent microscopy (spherical shape) & transmission electron microscopy (90-120 nm) respectively. The optimized 2 T-SLN gel showcases a skin-friendly profile with no significant signs of erythema and oedema and was found to be stable at room temperature for 2 months without any visual non-uniformity/cracking/breaking. In conclusion, the current research serves a new therapeutic perspective in assessing the activity of luliconazole for vaginal drug delivery using a 2 T-SLN gel system.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Formulation by design; Solid lipid nanoparticles; Thermosensitive; Transvaginal.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Aguin T.J., Sobel J.D. Vulvovaginal candidiasis in pregnancy. Current Infectious Disease Reports. 2015;17:30. - PubMed
-
- Anurova M.N., Bakhrushina E.O., Demina N.B. Review of contemporary gel-forming agents in the technology of dosage forms. Pharm. Chem. J. 2015;49:627–634.
-
- Attama A.A., Umeyor C.E. The use of solid lipid nanoparticles for sustained drug release. Therapeutic delivery. 2015;6:669–684. - PubMed
-
- Bhagat B., Desai P. Vulvovaginal candidiasis-an opportunistic infection in childbearing age group women, its isolation, identification and antibiotic profile. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015;4:1855–1859.
-
- Bhoop B.S. The pharma review; Nov-Des: 2013. An Autobiographical Account on Formulation by Design (FbD) pp. 36–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

