Prevalence of Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease in China: An Updated Systematical Analysis
- PMID: 33424580
- PMCID: PMC7793643
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.603854
Prevalence of Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease in China: An Updated Systematical Analysis
Abstract
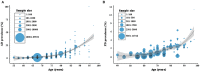
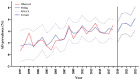
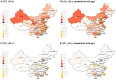
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are two major neurodegenerative diseases worldwide. Demographic aging is in rapid progress in China. Up-to-date estimates of AD and PD prevalence have not been provided. Methods: Studies that reported the prevalence of AD and PD in China were identified via a systematic database search from 1985 to 2018. Meta-analysis, local polynomial regression and autoregressive integrated moving average model were used for analyses. Results: A total of 99 studies were included in the study with populations of 385,312 and 227,228, respectively for AD and PD. The overall prevalence of AD and PD following age standardization was 3.20% [95% confidence interval (CI) = 3.17-3.23] and 1.06% (95% CI = 1.02-1.10), respectively in individuals over 60 years old. The rates increased drastically for every 10-years increment of age. The yearly prevalence of AD was predicted to increase from 3.81 to 6.17% in the next 5 years. Significant differences were observed between genders [male to female odds ratio (OR) for AD = 0.57, 95% CI = 0.51-0.64; OR for PD = 1.25, 95% CI = 1.06-1.46], and between education levels (Illiterate to non-illiterate OR for AD = 2.99, 95% CI = 2.38-3.75), but not between urban and rural settings. Conclusion: Our results provide an updated insight into the epidemiology of AD and PD in China and their associated rates and ratios. The findings may facilitate China policy makers and health professionals mitigate the related health issues.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; China; Parkinson's disease; epidemiology; prevalence; systematical analysis.
Copyright © 2020 Cui, Hou, Wu, Zuo, Lian, Zhang, Wang, Zhang and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chow N. (2006). The practice of filial piety and its impact on long-term care policies for elderly people in Asian Chinese communities. Asian J. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1, 31–35. Available online at: http://ajgg.org/image/module/ajgg_issue/1/31-T6.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

