Effects of Neurological Disorders on Bone Health
- PMID: 33424724
- PMCID: PMC7793932
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.612366
Effects of Neurological Disorders on Bone Health
Abstract
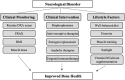
Neurological diseases, particularly in the context of aging, have serious impacts on quality of life and can negatively affect bone health. The brain-bone axis is critically important for skeletal metabolism, sensory innervation, and endocrine cross-talk between these organs. This review discusses current evidence for the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which various neurological disease categories, including autoimmune, developmental, dementia-related, movement, neuromuscular, stroke, trauma, and psychological, impart changes in bone homeostasis and mass, as well as fracture risk. Likewise, how bone may affect neurological function is discussed. Gaining a better understanding of brain-bone interactions, particularly in patients with underlying neurological disorders, may lead to development of novel therapies and discovery of shared risk factors, as well as highlight the need for broad, whole-health clinical approaches toward treatment.
Keywords: Neurology; PTSD; bone; depression; disease; mental health; osteoporosis.
Copyright © 2020 Kelly, Sidles and LaRue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alesci S., Martinez P. E., Kelkar S., Ilias I., Ronsaville D. S., Listwak S. J., et al. (2005). Major depression is associated with significant diurnal elevations in plasma interleukin-6 levels, a shift of its circadian rhythm, and loss of physiological complexity in its secretion: clinical implications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90 2522–2530. 10.1210/jc.2004-1667 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

