Glycemic Control Improvement in Italian Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes Followed Through Telemedicine During Lockdown Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33424771
- PMCID: PMC7793913
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.595735
Glycemic Control Improvement in Italian Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes Followed Through Telemedicine During Lockdown Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background/objective: To minimize the wide spread of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, Italy was placed in an almost complete lockdown state that forced people to "stay at home". Aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of lockdown on glycemic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D) followed through telemedicine.
Subjects/methods: This observational study involved patients with T1D using the real-time continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) Dexcom G6®. Ambulatory glucose profile data from the 3-months before schools closure (November 26, 2019-February 23, 2020; T0) and from the 3-months of consecutive lockdown (February 24-May 18, 2020; T1) were compared.
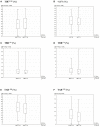
Results: Sixty-two children and adolescents (11.1 ± 4.37 years, 50% males) with T1D (median time disease 3.67 years) were enrolled in the study. Insulin total daily dose was unchanged, while time spent on physical activities was decreased (p<0.0001). Despite the lack of statistical significance, median value of the glucose management indicator decreased from 7.4% to 7.25%. Glucose standard deviation (p<0.0001) and coefficient of variation (p=0.001) improved across the study. Median time in range increased from 60.5% to 63.5% (p=0.008), time above range decreased from 37.3% to 34.1% (p=0.048), and time below range decreased from 1.85% to 1.45% (p=0.001).
Conclusions: Overall, in our children and adolescents with T1D glycemic control improved during lockdown. Despite patients were confined to their homes and limited to exercise, our data suggest that the use of real-time CGM, the continuous parental management, and the telemedicine can display beneficial effects on T1D care.
Keywords: COVID-19; children and adolescents; continuous glucose monitoring system; glycemic control; telemedicine—utilization; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2020 Predieri, Leo, Candia, Lucaccioni, Madeo, Pugliese, Vivaccia, Bruzzi and Iughetti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) “WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. Available at: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re... (Accessed August 3, 2020).
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/ (Accessed August 17, 2020).
-
- Department of Civil Protection COVID-19 case update. Available at: http://opendatadpc.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/b0c68bc... (Accessed August 17, 2020).
-
- Emilia-Romagna Region Coronavirus: measurements in Emilia-Romagna. Info-graphics. Available at: https://www.regione.emilia-romagna.it/coronavirus/infografiche (Accessed August 17, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

