Anti-quorum Sensing and Protective Efficacies of Naringin Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection in Danio rerio
- PMID: 33424802
- PMCID: PMC7793879
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.600622
Anti-quorum Sensing and Protective Efficacies of Naringin Against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection in Danio rerio
Abstract
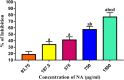
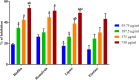
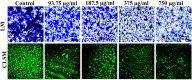
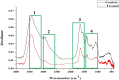
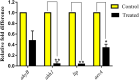
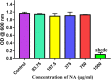
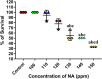
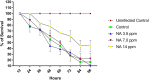
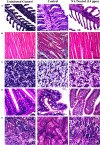
It is now well known that the quorum sensing (QS) mechanism coordinates the production of several virulence factors and biofilm formation in most pathogenic microorganisms. Aeromonas hydrophila is a prime pathogen responsible for frequent outbreaks in aquaculture settings. Recent studies have also continuously reported that A. hydrophila regulates virulence factor production and biofilm formation through the QS system. In addition to the presence of antibiotic resistance genes, biofilm-mediated antibiotic resistance increases the severity of A. hydrophila infections. To control the bacterial pathogenesis and subsequent infections, targeting the QS mechanism has become one of the best alternative methods. Though very few compounds were identified as QS inhibitors against A. hydrophila, to date, the screening and identification of new and effective natural QS inhibitors is a dire necessity to control the infectious A. hydrophila. The present study endorses naringin (NA) as an anti-QS and anti-infective agent against A. hydrophila. Initially, the NA showed a concentration-dependent biofilm reduction against A. hydrophila. Furthermore, the results of microscopic analyses and quantitative virulence assays displayed the promise of NA as a potential anti-QS agent. Subsequently, the downregulation of ahh1, aerA, lip and ahyB validate the interference of NA in virulence gene expression. Furthermore, the in vivo assays were carried out in zebrafish model system to evaluate the anti-infective potential of NA. The outcome of the immersion challenge assay showed that the recovery rate of the zebrafish has substantially increased upon treatment with NA. Furthermore, the quantification of the bacterial load upon NA treatment showed a decreased level of bacterial counts in zebrafish when compared to the untreated control. Moreover, the NA treatment averts the pathogen-induced histoarchitecture damages in vital organs of zebrafish, compared to their respective controls. The current study has thus analyzed the anti-QS and anti-infective capabilities of NA and could be employed to formulate effective treatment measures against A. hydrophila infections.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; biofilm; naringin; quorum sensing; virulence factors; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 Srinivasan, Devi, Santhakumari, Kannappan, Chen, Ravi and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Afifi S., Al-Thobiati S., Hazaa M. (2000). Bacteriological and histopathological studies on Aeromonas hydrophila infection of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from fish farms in Saudi Arabia. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 42 195–205.
-
- Alexpandi R., Prasanth M. I., Ravi A. V., Balamurugan K., Durgadevi R., Srinivasan R., et al. (2019). Protective effect of neglected plant Diplocyclos palmatus on quorum sensing mediated infection of Serratia marcescens and UV-A induced photoaging in model Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 201:111637. 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111637 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

