Vitis labrusca Extract (HP01) Improves Blood Circulation and Lipid Metabolism in Hyperlipidemic Rats
- PMID: 33424986
- PMCID: PMC7781693
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6180310
Vitis labrusca Extract (HP01) Improves Blood Circulation and Lipid Metabolism in Hyperlipidemic Rats
Abstract
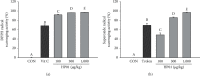
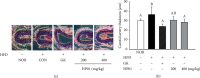
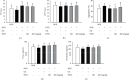
Excessive intake of high-lipid foods and lifestyle changes can easily cause hyperlipidemia. Hyperlipidemia is clinically considered a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the second leading cause of death worldwide. In this study, the effects of a Vitis labrusca extract (HP01) on coagulation, platelet aggregation, and lipid metabolism were investigated in hyperlipidemic rats. A rat model of high-fat diet- (HFD-) induced hyperlipidemia was used. Hemostatic parameters and lipid levels were investigated after HP01 treatment of hyperlipidemic rats. Different doses of HP01 (200 mg/kg/day and 400 mg/kg/day, p.o.) were administered for 3 weeks, and prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), and platelet aggregation and bleed time (BT) were determined. The levels of thromboxane B(2) (TXB(2)) and serotonin were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. Simultaneously, hepatic function and blood fat indexes, including aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), triglyceride (TG), malondialdehyde (MDA), and glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were also measured. In comparison with the data obtained for rats in the untreated HFD group, HP01 (200 mg/kg) treatment prolonged PT but did not affect aPTT. HP01 treatment did not alter plasma TXB(2), PGI2, or serotonin levels. However, HP01 showed some effects in improving liver function by reducing the levels of hepatic lipids. ALT, MDA, and hepatic TG levels significantly decreased, whereas GSH, GPx, CAT, and SOD levels significantly increased. These results confirm the HP01 extract will improve thromboplastic and the liver metabolic disorders in hyperlipidemia by oxidative stress response.
Copyright © 2020 Bo Yoon Chang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of astaxanthin on blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and platelet aggregation in hyperlipidemic rats.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):663-672. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1261905. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 27951728 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of oral selenium and magnesium co-supplementation on lipid metabolism, antioxidative status, histopathological lesions, and related gene expression in rats fed a high-fat diet.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 21;17(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0815-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30031400 Free PMC article.
-
[Acupuncture improves hepatic lipid metabolism by suppressing oxidative stress in obese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Mar 25;44(3):189-94. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180650. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 30945501 Chinese.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of the ethanol extract of Vitis thunbergii on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats through anti-oxidative activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Aug 1;142(3):795-803. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22698911
-
Antiobesity, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism, and Attenuation of Liver Oxidative Stress Effects of Hydroxy-α-sanshool Isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum on High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Aug 27;2019:5852494. doi: 10.1155/2019/5852494. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31534622 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Characteristics of cerebral ischemic stroke based on moyamoya disease and atherosclerosis-associated intracranial arterial stenosis.Neurol Sci. 2022 Feb;43(2):1087-1096. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05359-z. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34106367
-
Nutraceuticals as Modulators of Molecular Placental Pathways: Their Potential to Prevent and Support the Treatment of Preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 13;25(22):12167. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212167. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative CVD Collaborators. The changing patterns of cardiovascular diseases and their risk factors in the states of India: the global burden of disease study 1990–2016. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(12):e1339–e1351. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32172-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

