Comparison of fibrin sealants in peripheral vascular surgery: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 33425351
- PMCID: PMC7782199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.12.003
Comparison of fibrin sealants in peripheral vascular surgery: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Evidence comparing fibrin sealants (FSs) in surgery are limited. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of FSs, and manual compression in peripheral vascular surgery.
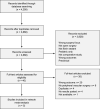
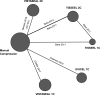
Methods: A systematic review of randomized trials was conducted in Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases within the last 15 years. Data were available to conduct a network meta-analysis (NMA) in peripheral vascular surgery. Fibrin sealant treatment arms were further broken-down and assessed by clotting time (i.e., 2-min [2C] or 1-min [1C]). The primary efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients achieving hemostasis by 4 min (T4). Treatment-related serious and non-serious adverse events (AEs) were qualitatively assessed.
Results: Five studies (n = 693), were included in the NMA. Results predicted VISTASEAL 2C, followed by EVICEL 1C, had the highest probability of achieving T4. Compared with manual compression, significant improvements in T4 were found with VISTASEAL 2C (relative risk [RR] = 2.67, 95% CrI: 2.13-3.34), EVICEL 1C (RR = 2.58, 95% CrI: 2.04-3.23), VISTASEAL 1C (RR = 2.00, 95% CrI: 1.45-2.65), and TISSEEL 2C (RR = 1.99, 95% CrI: 1.48-2.60). TISSEEL 1C was not significantly different than manual compression (RR = 1.40, 95% CrI: 0.70-2.33). Among FSs, VISTASEAL 2C was associated with a significant improvements in T4 compared with VISTASEAL 1C (RR = 1.33, 95% CrI: 1.02-1.82), TISSEEL 2C (RR = 1.34, 95% CrI: 1.05-1.77), and TISSEEL 1C (RR = 1.90, 95% CrI: 1.18-3.74). Treatment-related serious and non-serious AE rates were typically lower than 2%.
Conclusions: In peripheral vascular surgeries, VISTASEAL 2C and EVICEL 1C were shown to have the highest probabilities for achieving rapid hemostasis among the treatments compared. Future studies should expand networks across surgery types as data become available.
Keywords: Fibrin tissue adhesive; Hemostasis; Network meta-analysis; Systematic review; Vascular surgical procedures.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
CRG-EVERSANA (N. Ferko, D. Garcia, and A. Hogan) was provided consulting fees from 10.13039/100009933Ethicon Inc., for analysis and development of the manuscript. W. Danker III and A. DeAnglis are employees of Ethicon Inc., the manufacturer for VISTASEAL and EVICEL.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fibrin Sealant TISSEEL Lyo as a haemostatic agent in vascular surgery: Results of randomized, controlled, patient-blinded, multicentre clinical study in the Russian population.Sci Prog. 2023 Jul-Sep;106(3):368504231182834. doi: 10.1177/00368504231182834. Sci Prog. 2023. PMID: 37427979 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fibrin and Thrombin Sealants in Vascular and Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020 Sep;60(3):469-478. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2020.05.016. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32620348
-
A comparison of the mechanical, kinetic, and biochemical properties of fibrin clots formed with two different fibrin sealants.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011 Jan;22(1):19-23. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e32833fcbfb. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011. PMID: 21150581
-
Fibrin sealant (evicel® [quixil®/crosseal™]): a review of its use as supportive treatment for haemostasis in surgery.Drugs. 2011 Oct 1;71(14):1893-915. doi: 10.2165/11207700-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21942978 Review.
-
Bleeding-Related Complications and Readmission Rates Associated With Fibrin Sealant Use in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery in the United States.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017 Jun;31(3):876-882. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2016.11.015. Epub 2016 Nov 10. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017. PMID: 28320573
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of sFilm-FS, a novel biodegradable fibrin sealant, in Göttingen minipigs.J Toxicol Pathol. 2021 Oct;34(4):319-330. doi: 10.1293/tox.2021-0030. Epub 2021 Jul 10. J Toxicol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34629733 Free PMC article.
-
The role of sealants for achieving anastomotic hemostasis in vascular surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5(5):CD013421. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013421.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38695613 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional bio-derived materials for biomedical applications: challenges and opportunities.RSC Adv. 2025 Mar 28;15(12):9375-9397. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07531e. eCollection 2025 Mar 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40161530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative high-resolution physicochemical analysis of commercially available fibrin sealants: Impact of sealant osmolality on biological performance.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023 Apr;111(4):488-501. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37466. Epub 2022 Nov 10. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023. PMID: 36355631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyasaka Y., Barnes M.E., Gersh B.J., Cha S.S., Bailey K.R., Abhayaratna W.P., Seward J.B., Tsang T.S. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114:119–125. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

