Diabetes Insipidus: A Pragmatic Approach to Management
- PMID: 33425560
- PMCID: PMC7785480
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12498
Diabetes Insipidus: A Pragmatic Approach to Management
Abstract
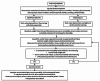
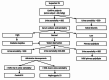
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a disorder of water balance characterized by polyuria and polydipsia. It can occur due to genetic and acquired causes that affect the secretion or action of arginine vasopressin (AVP) or antidiuretic hormone (ADH).Markedly increased thirst and urination are not only quite distressing but also increases the risk of volume depletion and hypernatremia in severe situations. A careful diagnosis of the type of DI and its etiology is based on careful clinical evaluation, measurement of urine and serum osmolality, and water deprivation test. Management includes the correction of any water deficit and the use of specific pharmacological agents, including desmopressin, thiazides, and amiloride.
Keywords: central diabetes insipidus; desmopressin; diabetes insipidus; nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Copyright © 2021, Priya et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Diabetes insipidus - diagnosis and management. Di Iorgi N, Napoli F, Allegri AEM, et al. Horm Res Paediatr. 2012;77:69–84. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and treatment of hypernatremia. Muhsin SA, Mount DB. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;30:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes insipidus in infants and children. Dabrowski E, Kadakia R, Zimmerman D, et al. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;30:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Genetics of diabetes insipidus. Schernthaner-Reiter MH, Stratakis CA, Luger A. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2017;46:305–334. - PubMed
-
- Sarma KV. Medicine Update. Vol. 23. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd; 2013. Algorithmic approach for the diagnosis of polyuria; pp. 311–313.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous