Use of the Profunda Femoris Artery Perforator Flap for Reconstruction after Sarcoma Resection
- PMID: 33425601
- PMCID: PMC7787329
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003289
Use of the Profunda Femoris Artery Perforator Flap for Reconstruction after Sarcoma Resection
Abstract
Soft tissue sarcomas are rare neoplasms that can occur on any part of the body. The operative position for the resection is determined depending on the site of the soft tissue sarcomas; intraoperative repositioning may be needed for reconstruction. We present the profunda femoris artery perforator (PAP) flap harvest technique (wherein the flap can be used in any position), and suggest that the PAP flap transfer can eliminate the need for intraoperative repositioning.
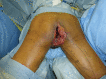
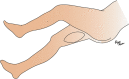
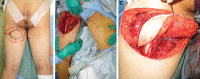
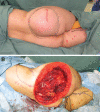
Methods: From December 2018 to January 2020, 7 patients with an average age of 68 years underwent reconstructions using a PAP flap after wide resection of STS. The mean defect size was 11.3 × 16.5 cm (range, 5.5-25 × 11-26 cm). The location of the defects was the medial thigh in 2 patients, the posterior thigh in 1, the popliteal fossa in 1, the groin in 1, and the buttock in 2. The PAP flap was elevated in the supine "frog-leg" position, the prone position, the jack-knife position, or the lateral "crisscross" position; the lateral decubitus position with the donor lower extremity on the bottom.
Results: Of the 7 cases, the operations were performed in the supine "frog-leg" position in 3 cases, the prone position in 2 cases, the jack-knife position in 1 case, and the lateral "crisscross" position in 1 case. There were no intraoperative position changes in all cases. The mean size of the PAP flap was 8.7 × 19.9 cm (range, 6-11 × 17-24 cm). One patient had donor site dehiscence, which was treated conservatively. The PAP flaps survived completely in all cases. The mean follow-up period was 10.5 months (range, 6-17 months).
Conclusion: Since the PAP flap elevation is feasible in every position, the PAP flap can be considered a versatile reconstruction option after sarcoma resection.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Forte AJ, Oliver JD, McRae M, et al. Use of the subscapular system by maintaining unilateral decubitus placement without repositioning in microvascular free tissue transplantation. Microsurgery. 2020;40:125–129. - PubMed
-
- Angrigiani C, Grilli D, Thorne CH. The adductor flap: a new method for transferring posterior and medial thigh skin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:1725–1731. - PubMed
-
- Allen RJ, Haddock NT, Ahn CY, et al. Breast reconstruction with the profunda artery perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:16e–23e. - PubMed
-
- Karakawa R, Yoshimatsu H, Fuse Y, et al. The correlation of the perforators and the accessory saphenous vein in a profunda femoris artery perforator flap for additional venous anastomosis: a cadaveric study and clinical application. Microsurgery. 2020;40:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Scaglioni MF, Kuo YR, Yang JC, et al. The posteromedial thigh flap for head and neck reconstruction: anatomical basis, surgical technique, and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136:363–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
