Anticancer evaluation of N-benzoyl-3-allylthiourea as potential antibreast cancer agent through enhances HER-2 expression
- PMID: 33425698
- PMCID: PMC7784947
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_77_20
Anticancer evaluation of N-benzoyl-3-allylthiourea as potential antibreast cancer agent through enhances HER-2 expression
Abstract
Breast cancer with HER-2 overexpression is sensitive to drugs which target the receptor or its kinase activity. Although the anti-HER-2 therapies commonly used have improved patient outcome, resistance usually occurs. In this present study, we investigated a modification of the chemical structure of allylthiourea derivatives in order to enhance the cytotoxicity effect on breast cancer cells with HER-2 overexpression. The aim of this research was to predict the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity by in silico study and to explore the effect N-benzoyl-3-allylthiourea (BATU) on MCF-7 cell line with overexpressing of HER-2 using MTT assay and western blot. The result showed that the cytotoxicity effects of BATU on MCF-7/HER-2 cell line (IC50 value 0.64 mM) were higher than on MCF-7 cell lines (IC50 value 1.47 mM). In addition, the cytotoxic effects of BATU on MCF-7 and MCF-7/HER-2 were higher than allylthiourea as a lead compound (IC50 value 5.22 and 3.17 mM). The results also confirmed that the BATU compound has the ability to effectively enhance its cytotoxicity against MCF-7/HER-2 through enhanced HER-2 expression and inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) activation. Above all, the BATU compound is effective in increasing HER-2 expression and inactivating NF-kB transcription factors, thereby resulting in inhibition of protein expression which works a significant part in cell proliferation. Therefore, the BATU compound has the potential to be developed as a complementary drug in breast cancer therapy with HER-2 positive.
Keywords: Allylthiourea; HER-2; MCF-7; N-benzoyl-3-allylthiourea; cytotoxicity; nuclear factor kappa B.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

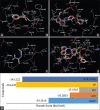
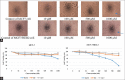
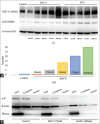
References
-
- Laskin JJ, Sandler AB. Epidermal growth factor receptor: A promising target in solid tumours. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;30:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Johnston SR, Leary A. Lapatinib: A novel EGFR/HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor for cancer. Drugs Today (Barc) 2006;42:441–53. - PubMed
-
- Mitra D, Brumlik MJ, Okamgba SU, Zhu Y, Duplessis TT, Parvani JG, et al. An oncogenic isoform of HER2 associated with locally disseminated breast cancer and trastuzumab resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2152–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
