Connexins in Lung Cancer and Brain Metastasis
- PMID: 33425756
- PMCID: PMC7786366
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.599383
Connexins in Lung Cancer and Brain Metastasis
Abstract
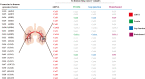
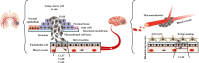
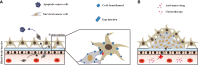
Connexins (Cxs) are involved in the brain metastasis of lung cancer cells. Thus, it is necessary to determine whether gap junction-forming Cxs are involved in the communication between lung cancer cells and the host cells, such as endothelial cells, forming the brain-blood-barrier, and cells in the central nervous system. Data from multiple studies support that Cxs function as tumor suppressors during lung cancer occurrence. However, recent evidence suggests that during metastasis to the brain, cancer cells establish communication with the host. This review discusses junctional or non-junctional hemichannel studies in lung cancer development and brain metastasis, highlighting important unanswered questions and controversies.
Keywords: astrocytes; connexin; endothelial cells; gap junction; hemichannel; lung cancer brain metastasis.
Copyright © 2020 Luo, Chen, Yang, Huang, Cardenas and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aasen T, Sansano I, Montero MA, Romagosa C, Temprana-Salvador J, Martinez-Marti A, et al. Insight into the Role and Regulation of Gap Junction Genes in Lung Cancer and Identification of Nuclear Cx43 as a Putative Biomarker of Poor Prognosis. Cancers (Basel) (2019) 11:1–20. 10.20944/preprints201902.0109.v1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

