Effectiveness of Gentle Human Touch for Pain Control During Examination for Retinopathy of Pre-maturity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33425819
- PMCID: PMC7793661
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.608378
Effectiveness of Gentle Human Touch for Pain Control During Examination for Retinopathy of Pre-maturity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
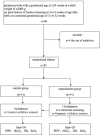
Background: Retinopathy of pre-maturity (ROP) is a disorder of the retinal blood vessels in pre-term infants with low birth weight. It is a leading cause of blindness in children. During ROP screening, the use of mydriatic drops and eyelid openers causes pain and discomfort. Pain management strategies include medications and behavioral interventions. The objectives of this study was to investigate the effects of Gentle Human Touch on pain in pre-term infants undergoing screening for ROP. Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, 82 infants in the neonatal intensive care unit at Children's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University who met the ROP screening criteria were randomly assigned to experimental and control groups using the random number table. The infants in the experimental group continuously received Gentle Human Touch during screening, while those in the control group were screened according to the routine procedure. All neonates were administered local eye anesthesia before the screening. The degree of pain was assessed using the Pre-mature Infant Pain Profile score. A double-channel near-infrared spectroscopy device was used to monitor regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rScO2), while oxygen saturation (SaO2) and heart rate were measured using pulse oximetry. The Pre-mature Infant Pain Profile score was the primary outcome, while heart rate, SaO2, and rScO2 were the secondary outcomes. Results: The gestational age, corrected gestational age, birth weight, and Apgar score at examination and the basal heart rate, SaO2, and rScO2 showed no significant intergroup differences (P > 0.05 for all). Both groups demonstrated significant decreases in SaO2 and rScO2 in response to the examination (P < 0.05 for all). During the examination, the Pre-mature Infant Pain Profile score (14.82 ± 3.22 vs. 9.29 ± 2.89, respectively; P < 0.05) was significantly higher in the control group than in the experimental group, while rScO2 (57.61 ± 3.51 vs. 54.76 ± 4.54%, respectively; P < 0.05) and SaO2 (91.89 ± 6.43 vs. 85.68 ± 8.31%; P < 0.05) were significantly higher in the experimental group than in the control group. There was no significant difference in heart rate changes between the two groups before and after the examination (182.60 ± 3.50 vs. 170.80 ± 3.50 time/min; P > 0.05). Conclusions: The findings of this study suggest that Gentle Human Touch can effectively alleviate pain during ROP screening in pre-mature infants. Clinical Trial Registration: ISRCTN10976481, Registered 06 March 2020, Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: neonates; pain; retinopathy of pre-maturity; screening; touch intervention.
Copyright © 2020 Sun, Zhang, Chen, Yang, Qiu, Lu and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous