Adsorption of Orange II Onto Zn2Al-Layered Double Hydroxide Prepared From Zinc Ash
- PMID: 33425845
- PMCID: PMC7793787
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.573535
Adsorption of Orange II Onto Zn2Al-Layered Double Hydroxide Prepared From Zinc Ash
Abstract
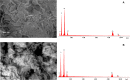
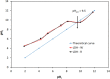
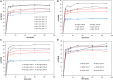
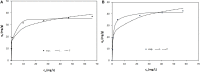
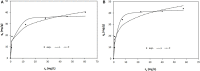
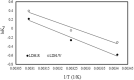
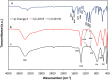
The dye industry is one of the largest water consuming industries, and at the same time generates large quantities of wastewaters. The resulting wastewaters require proper treatment before discharge, because the dye contents have a negative effect on the water body and organisms present in it. The most efficient treatment method for water containing dyes is represented by adsorption processes. The challenge with these adsorption processes is to develop new, efficient, viable, and economic adsorbent materials. Therefore, in the present paper, the performance of Zn2Al-layered double hydroxide, prepared from an industrial waste (zinc ash) as a zinc source, was investigated in the Orange II dye adsorption process. The Zn2Al-layered double hydroxide prepared from secondary sources presents similar morphological and structural characteristics as those prepared from analytical grade reagents. The influence of initial dye concentration, adsorption time, solid:liquid ratio, pH, and temperature was evaluated in order to confirm the benefit of this waste valorization. A comparison with the reference Zn2Al-layered double hydroxide prepared from analytical grade reagents was performed and the results show that due to the small presence of impurities, the material prepared from zinc ash shows better adsorption capacities (qmax,exp = 42.5 mg/g at 293 K) than the material prepared from reagents (qmax,exp = 36.9 mg/g at 293 K), justifying the utilization of secondary sources for layered double hydroxides preparation. The proposed treatment process presents advantages from both economic and environmental protection point of view.
Keywords: Orange II adsorption; equilibrium; kinetics; layered double hydroxides; thermodynamics; zinc ash waste.
Copyright © 2020 Tǎmaş, Cozma, Cocheci, Lupa and Rusu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abramian L., El-Rassy H. (2009). Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of azo-dye orange II onto highly porous titania aerogel. Chem. Eng. J. 150, 403–410. 10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.019 - DOI
-
- Aguiar J. E., Bezerra B. T. C., de Melo Braga B., da Silva Lima P. D., Nogueira R. E. F. Q., de Lucena S. M. P., et al. (2013). Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution on non-calcined Mg-Al layered double hydroxide: experimental and theoretical study. Sep. Sci. Technol. 48, 2307–2316. 10.1080/01496395.2013.804837 - DOI
-
- Asfaram A., Ghaedi M., Agarwal S., Tyagi I., Kumar Gupta V. (2015). Removal of basic dye Auramine-O by ZnS:Cu nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: optimization of parameters using response surface methodology with central composite design. RSC Adv. 5, 18438–18450. 10.1039/C4RA15637D - DOI
-
- Banerjee S., Chattopadhyaya M. S. (2017). Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low cost agricultural by-product. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S1629–S1638. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.06.005 - DOI
-
- Barik G., Padhan E., Dash B., Sarangi K., Subbaiah T. (2014). Preparation of layered nickel aluminium double hydroxide from waste solution of nickel. Miner. Eng. 69, 107–112. 10.1016/j.mineng.2014.07.015 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

