Design and Optimization of Quinazoline Derivatives: New Non-nucleoside Inhibitors of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus
- PMID: 33425849
- PMCID: PMC7793975
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.590235
Design and Optimization of Quinazoline Derivatives: New Non-nucleoside Inhibitors of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus
Abstract
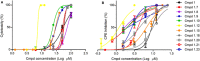
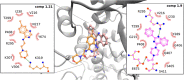
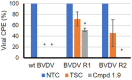
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) belongs to the Pestivirus genus (Flaviviridae). In spite of the availability of vaccines, the virus is still causing substantial financial losses to the livestock industry. In this context, the use of antiviral agents could be an alternative strategy to control and reduce viral infections. The viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is essential for the replication of the viral genome and constitutes an attractive target for the identification of antiviral compounds. In a previous work, we have identified potential molecules that dock into an allosteric binding pocket of BVDV RdRp via a structure-based virtual screening approach. One of them, N-(2-morpholinoethyl)-2-phenylquinazolin-4-amine [1, 50% effective concentration (EC50) = 9.7 ± 0.5 μM], was selected to perform different chemical modifications. Among 24 derivatives synthesized, eight of them showed considerable antiviral activity. Molecular modeling of the most active compounds showed that they bind to a pocket located in the fingers and thumb domains in BVDV RdRp, which is different from that identified for other non-nucleoside inhibitors (NNIs) such as thiosemicarbazone (TSC). We selected compound 2-[4-(2-phenylquinazolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanol (1.9; EC50 = 1.7 ± 0.4 μM) for further analysis. Compound 1.9 was found to inhibit the in vitro replication of TSC-resistant BVDV variants, which carry the N264D mutation in the RdRp. In addition, 1.9 presented adequate solubility in different media and a high-stability profile in murine and bovine plasma.
Keywords: BVDV inhibitors; RdRp protein; molecular dynamics; pharmacokinetics in vitro properties; quinazoline derivatives.
Copyright © 2020 Fernández, Castro, Rosas, Fidalgo, Adler, Battini, España de Marco, Fabiani, Bruno, Bollini and Cavallaro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Quinolinecarboxamides Inhibit the Replication of the Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus by Targeting a Hot Spot for the Inhibition of Pestivirus Replication in the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase.Molecules. 2020 Mar 12;25(6):1283. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061283. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32178258 Free PMC article.
-
Substituted 2,6-bis(benzimidazol-2-yl)pyridines: a novel chemical class of pestivirus inhibitors that targets a hot spot for inhibition of pestivirus replication in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.Antiviral Res. 2014 Jun;106:71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24680957
-
Stability of the resistance to the thiosemicarbazone derived from 5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone, a non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitor of bovine viral diarrhea virus.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 20;9(6):e100528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100528. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24950191 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Potent Non-nucleoside Inhibitors of Dengue Viral RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Fragment Screening and Structure-Guided Design.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1062:187-198. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8727-1_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29845534 Review.
-
What is known about the antiviral agents active against bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV)?Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(26):2933-55. doi: 10.2174/092986710792065036. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20858174 Review.
Cited by
-
Template Entrance Channel as Possible Allosteric Inhibition and Resistance Site for Quinolines Tricyclic Derivatives in RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;16(3):376. doi: 10.3390/ph16030376. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986476 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticorrosion Activities of 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]quinazolinone.Molecules. 2023 Jul 11;28(14):5340. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145340. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513216 Free PMC article.
-
Matrine and icariin can inhibit bovine viral diarrhoea virus replication by promoting type I interferon response in vitro.J Vet Res. 2024 Mar 23;68(1):35-44. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2024-0013. eCollection 2024 Mar. J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38525227 Free PMC article.
-
Codonopsis pilosula Polysaccharides Exert Antiviral Effect Through Activating Immune Function in a Macrophage Model of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Infection.Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 27;12(5):415. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050415. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431508 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Inhibits Hsp70 Blocking of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Infection and Replication in the Early Stage of Virus Infection.Viruses. 2022 Oct 26;14(11):2365. doi: 10.3390/v14112365. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36366463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asthana S., Shukla S., Vargiu A. V., Ceccarelli M., Ruggerone P., Paglietti G., et al. . (2013). Different molecular mechanisms of inhibition of bovine viral diarrhea virus and hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases by a novel benzimidazole. Biochemistry 52, 3752–3764. 10.1021/bi400107h - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

