The Role of Complement in Myocardial Infarction Reperfusion Injury: An Underappreciated Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 33425913
- PMCID: PMC7793727
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.606407
The Role of Complement in Myocardial Infarction Reperfusion Injury: An Underappreciated Therapeutic Target
Abstract
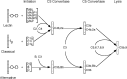
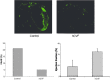
This article reviews the pathogenetic role of the complement system in myocardial infarction reperfusion injury. The complement activation pathways involved in myocardial tissue injury are identified, as are the complement-derived effector molecules. The results of past anti-complement therapies are reviewed; as the more recent therapeutic concept of complement depletion with humanized CVF described.
Keywords: cobra venom factor; complement; complement depletion; humanized cobra venom factor; myocardial infarction; reperfusion injury.
Copyright © 2020 Vogel.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has a financial interest in iC3 LLC of Sunnyvale, CA, a company that develops therapeutics for complement depletion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cobra venom factor: Structure, function, and humanization for therapeutic complement depletion.Toxicon. 2010 Dec 15;56(7):1198-222. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.04.007. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 20417224 Review.
-
Humanized cobra venom factor decreases myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Mol Immunol. 2009 Dec;47(2-3):506-10. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.08.017. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19747734 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized cobra venom factor: structure, activity, and therapeutic efficacy in preclinical disease models.Mol Immunol. 2014 Oct;61(2):191-203. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.06.035. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25062833 Review.
-
Complement depletion with humanised cobra venom factor: efficacy in preclinical models of vascular diseases.Thromb Haemost. 2015 Mar;113(3):548-52. doi: 10.1160/TH14-04-0300. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25031089 Review.
-
Humanized cobra venom factor: experimental therapeutics for targeted complement activation and complement depletion.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(28):2916-26. doi: 10.2174/138161207782023748. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17979736 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiomyocyte-derived circulating extracellular vesicles allow a non-invasive liquid biopsy of myocardium in health and disease.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 22:2024.09.19.24314009. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.19.24314009. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39371135 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The Role of B Cells in Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022 Aug;24(8):935-946. doi: 10.1007/s11886-022-01722-4. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35689723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Hydrophilic Modification of Synthetic Dialysis Membranes on Hemocompatibility and Performance.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Sep 26;12(10):932. doi: 10.3390/membranes12100932. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cobra Venom Factor Boosts Arteriogenesis in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 30;23(15):8454. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158454. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955584 Free PMC article.
-
The heart-bone connection: relationships between myocardial infarction and osteoporotic fracture.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):H845-H856. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00576.2023. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38305753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong P. W., Mahaffey K. W., Chang W.-C., Weaver W. D., Hochmann J. S., Theroux P., et al. (2006). Concerning the mechanism of pexelizumab’s benefit in acute myocardial infarction. Amer. Heart J. 151 787–790. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira R. (2010). The reduction of infarct size – forty years of research. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 29 1037–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

