Establishment and Characterization of a Topotecan Resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCI-H460/TPT10 Cell Line
- PMID: 33425914
- PMCID: PMC7786180
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.607275
Establishment and Characterization of a Topotecan Resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCI-H460/TPT10 Cell Line
Abstract
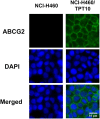
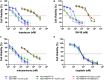
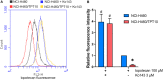
While topotecan (TPT) is a first- and second-line chemotherapeutic drug in treating lung cancer, the development of drug resistance in tumors still reserves as a major obstacle to chemotherapeutic success. Therefore, a better understanding of the mechanisms of topotecan resistance is critical. In this study, the first topotecan-resistant human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line, termed NCI-H460/TPT10, was established from the parental NCI-H460 cell line. NCI-H460/TPT10 cells exhibited a 394.7-fold resistance to TPT, and cross-resistance to SN-38, mitoxantrone, and doxorubicin, compared to parental NCI-H460 cells. Overexpression of ABCG2 localized on the cell membrane, but not ABCB1 or ABCC1, was found in NCI-H460/TPT10 cells, indicating that ABCG2 was likely to be involved in topotecan-resistance. This was confirmed by the abolishment of drug resistance in NCI-H460/TPT10 cells after ABCG2 knockout. Moreover, the involvement of functional ABCG2 as a drug efflux pump conferring multidrug resistance (MDR) was indicated by low intracellular accumulation of TPT in NCI-H460/TPT10 cells, and the reversal effects by ABCG2 inhibitor Ko143. The NCI-H460/TPT10 cell line and its parental cell line can be useful for drug screening and developing targeted strategies to overcome ABCG2-mediated MDR in NSCLC.
Keywords: ABCG2; NCI-H460/TPT10; multidrug resistance; non-small cell lung cancer; topotecan.
Copyright © 2020 Lei, Teng, Zhang, Fan, Wang, Cai, Lu, Yang, Wurpel and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Y.-L., Yang T.-Y., Chen K.-C., Wu C.-L., Hsu S.-L., Hsueh C.-M. (2016). Hypoxia can impair doxorubicin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting MRP1 and P-gp expression and boosting the chemosensitizing effects of MRP1 and P-gp blockers. Cell. Oncol. 39 411–433. 10.1007/s13402-016-0285-5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

