A Dynamic Role of Mastermind-Like 1: A Journey Through the Main (Path)ways Between Development and Cancer
- PMID: 33425921
- PMCID: PMC7787167
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.613557
A Dynamic Role of Mastermind-Like 1: A Journey Through the Main (Path)ways Between Development and Cancer
Abstract
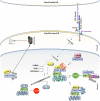
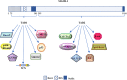
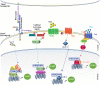
Major signaling pathways, such as Notch, Hedgehog (Hh), Wnt/β-catenin and Hippo, are targeted by a plethora of physiological and pathological stimuli, ultimately resulting in the modulation of genes that act coordinately to establish specific biological processes. Many biological programs are strictly controlled by the assembly of multiprotein complexes into the nucleus, where a regulated recruitment of specific transcription factors and coactivators on gene promoter region leads to different transcriptional outcomes. MAML1 results to be a versatile coactivator, able to set up synergistic interlinking with pivotal signaling cascades and able to coordinate the network of cross-talking pathways. Accordingly, despite its original identification as a component of the Notch signaling pathway, several recent reports suggest a more articulated role for MAML1 protein, showing that it is able to sustain/empower Wnt/β-catenin, Hh and Hippo pathways, in a Notch-independent manner. For this reason, MAML1 may be associated to a molecular "switch", with the function to control the activation of major signaling pathways, triggering in this way critical biological processes during embryonic and post-natal life. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge about the pleiotropic role played by MAML proteins, in particular MAML1, and we recapitulate how it takes part actively in physiological and pathological signaling networks. On this point, we also discuss the contribution of MAML proteins to malignant transformation. Accordingly, genetic alterations or impaired expression of MAML proteins may lead to a deregulated crosstalk among the pathways, culminating in a series of pathological disorders, including cancer development. Given their central role, a better knowledge of the molecular mechanisms that regulate the interplay of MAML proteins with several signaling pathways involved in tumorigenesis may open up novel opportunities for an attractive molecular targeted anticancer therapy.
Keywords: Hedgehog; Hippo; MAML; Notch; cancer; coactivator; development; signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2020 Zema, Pelullo, Nardozza, Felli, Screpanti and Bellavia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MAML1 regulates cell viability via the NF-κB pathway in cervical cancer cell lines.Exp Cell Res. 2011 Aug 1;317(13):1830-40. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 24. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21640102
-
Transcriptional mechanisms by the coregulator MAML1.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009 Dec;10(6):570-6. doi: 10.2174/138920309789630543. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19751190 Review.
-
Wnt, Notch, and TGF-β Pathways Impinge on Hedgehog Signaling Complexity: An Open Window on Cancer.Front Genet. 2019 Aug 21;10:711. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00711. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31552081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mastermind-like transcriptional co-activators: emerging roles in regulating cross talk among multiple signaling pathways.Oncogene. 2008 Sep 1;27(38):5138-47. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.228. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18758483 Review.
-
The Notch coactivator, MAML1, functions as a novel coactivator for MEF2C-mediated transcription and is required for normal myogenesis.Genes Dev. 2006 Mar 15;20(6):675-88. doi: 10.1101/gad.1383706. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16510869 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recurrent PTBP1::MAML2 fusions in composite hemangioendothelioma with neuroendocrine differentiation: A report of two cases involving neck lymph nodes.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2022 Apr;61(4):187-193. doi: 10.1002/gcc.23017. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34862698 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte activity of the cholesterol sensor smoothened regulates cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis in mice.iScience. 2021 Sep 4;24(9):103089. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103089. eCollection 2021 Sep 24. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34568800 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Import and Export of YAP and TAZ.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;15(20):4956. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204956. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch directs telencephalic development and controls neocortical neuron fate determination by regulating microRNA levels.Development. 2023 Jun 1;150(11):dev201408. doi: 10.1242/dev.201408. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Development. 2023. PMID: 37272771 Free PMC article.
-
Untying the Gordian knot of composite hemangioendothelioma: Discovery of novel fusions.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2024 Jan;63(1):e23198. doi: 10.1002/gcc.23198. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2024. PMID: 37658696 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

