From waste of marine culture to natural patch in cardiac tissue engineering
- PMID: 33426372
- PMCID: PMC7782558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.011
From waste of marine culture to natural patch in cardiac tissue engineering
Abstract
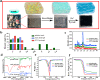
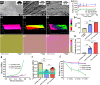
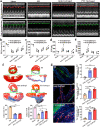
Sea squirt, as a highly invasive species and main biofouling source in marine aquaculture, has seriously threatened the biodiversity and aquaculture economy. On the other hand, a conductive biomaterial with excellent biocompatibility, and appropriate mechanical property from renewable resources is urgently required for tissue engineering patches. To meet these targets, we presented a novel and robust strategy for sustainable development aiming at the marine pollution via recycling and upgrading the waste biomass-sea squirts and serving as a renewable resource for functional bio-scaffold patch in tissue engineering. We firstly demonstrated that the tunic cellulose derived natural self-conductive scaffolds successfully served as functional cardiac patches, which significantly promote the maturation and spontaneous contraction of cardiomyocytes both in vitro and enhance cardiac function of MI rats in vivo. We believe this novel, feasible and "Trash to Treasure" strategy to gain cardiac patches via recycling the waste biomass must be promising and beneficial for marine environmental bio-pollution issue and sustainable development considering the large-scale consumption potential for tissue engineering and other applications.
Keywords: Biofouling; Cardiac tissue engineering; Cellulose; Myocardial infarction; Sea squirts.
© 2020 [The Author/The Authors].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chitosan/silk fibroin modified nanofibrous patches with mesenchymal stem cells prevent heart remodeling post-myocardial infarction in rats.Acta Biomater. 2018 Oct 15;80:154-168. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.013. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30218777
-
Engineering a naturally-derived adhesive and conductive cardiopatch.Biomaterials. 2019 Jul;207:89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.03.015. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 30965152 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospun conductive nanofibrous scaffolds for engineering cardiac tissue and 3D bioactuators.Acta Biomater. 2017 Sep 1;59:68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.06.036. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28663141
-
Tilapia fish waste: An asset for tissue engineering - A review.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2023 Nov-Dec;27(6):568-577. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_395_22. Epub 2024 Jan 24. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2023. PMID: 38434505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental impact of aquaculture and countermeasures to aquaculture pollution in China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2007 Nov;14(7):452-62. doi: 10.1065/espr2007.05.426. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2007. PMID: 18062476 Review.
Cited by
-
Materials Advances in Devices for Heart Disease Interventions.Adv Mater. 2025 Jul;37(27):e2420114. doi: 10.1002/adma.202420114. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40244561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cigarette filter-derived biomimetic cardiac niche for myocardial infarction repair.Bioact Mater. 2024 Feb 14;35:362-381. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.012. eCollection 2024 May. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38379697 Free PMC article.
-
Electroconductive biomaterials for cardiac tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2022 Feb;139:118-140. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.08.031. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 34455109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conductive Bacterial Nanocellulose-Polypyrrole Patches Promote Cardiomyocyte Differentiation.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 Jul 17;6(7):2860-2874. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00303. Epub 2023 Jun 21. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37342003 Free PMC article.
-
Avian Egg: A Multifaceted Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering.Ind Eng Chem Res. 2021 Dec 8;60(48):17348-17364. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.1c03085. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 35317347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoag H. Invaders leave enemies behind. Nature. 2003;6:1476–4687. doi: 10.1038/news030203-6. - DOI
-
- Lacoste E., Gaertner-Mazouni N. Biofouling impact on production and ecosystem functioning: a review for bivalve aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2015;7:187–196. doi: 10.1111/raq.12063. - DOI
-
- Kenworthy J.M., Davoult D., Lejeusne C. Compared stress tolerance to short-term exposure in native and invasive tunicates from the NE Atlantic: when the invader performs better. Marine Biology. 2018;165:164. doi: 10.1007/s00227-018-3420-1. - DOI
-
- Islam M.S., Haque M. The mangrove-based coastal and nearshore fisheries of Bangladesh: ecology, exploitation and management. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2004;14:153–180. doi: 10.1007/s11160-004-3769-8. - DOI
-
- Dunlop M.J., Bishnu A., Rabin B. Isolation of nanocrystalline cellulose from tunicates. J Environ Chem Eng. 2018;6:4408–4412. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.056. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

