Deep-LSTM ensemble framework to forecast Covid-19: an insight to the global pandemic
- PMID: 33426425
- PMCID: PMC7779101
- DOI: 10.1007/s41870-020-00571-0
Deep-LSTM ensemble framework to forecast Covid-19: an insight to the global pandemic
Abstract
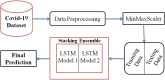
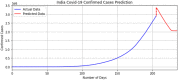
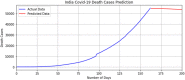
The pandemic of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is spreading all over the world. Medical health care systems are in urgent need to diagnose this pandemic with the support of new emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IoT) and Big Data System. In this dichotomy study, we divide our research in two ways-firstly, the review of literature is carried out on databases of Elsevier, Google Scholar, Scopus, PubMed and Wiley Online using keywords Coronavirus, Covid-19, artificial intelligence on Covid-19, Coronavirus 2019 and collected the latest information about Covid-19. Possible applications are identified from the same to enhance the future research. We have found various databases, websites and dashboards working on real time extraction of Covid-19 data. This will be conducive for future research to easily locate the available information. Secondly, we designed a nested ensemble model using deep learning methods based on long short term memory (LSTM). Proposed Deep-LSTM ensemble model is evaluated on intensive care Covid-19 confirmed and death cases of India with different classification metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, f-measure and mean absolute percentage error. Medical healthcare facilities are boosted with the intervention of AI as it can mimic human intelligence. Contactless treatment is possible only with the help of AI assisted automated health care systems. Furthermore, remote location self treatment is one of the key benefits provided by AI based systems.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Covid-19; Deep learning; LSTM; Nested ensemble.
© Bharati Vidyapeeth's Institute of Computer Applications and Management 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar D, Malviya R, Sharma PK. CoronaVirus: a review of COVID-19. EJMO. 2020;4(1):8–25. doi: 10.14744/ejmo.2020.51418. - DOI
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2003) Update: outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome-worldwide, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 52(12):241–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
