Early Clinical Evaluation of Percutaneous Full-endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Insertion for Treating Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- PMID: 33426744
- PMCID: PMC7862160
- DOI: 10.1111/os.12900
Early Clinical Evaluation of Percutaneous Full-endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Insertion for Treating Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the clinical efficacy of percutaneous full-endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (Endo-TLIF) with percutaneous pedicle screws (PPSs) performed by using a visualization system with that of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS-TLIF) for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).
Methods: From June 2017 to May 2018, the data of a total of 78 patients who met the selection criteria were retrospectively reviewed and were divided into the Endo-TLIF group (40 cases) and the MIS-TLIF group (38 cases) according to the surgical method used. The visual analog scale (VAS) and the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) scale were administered preoperatively and at the 1-week, 3-month, and 1-2-year follow-ups. The fusion rate and major complications, including revision, were also recorded.
Results: All the patients were followed up for 24 to 34 months, with an average follow-up of 30.7 months. The intraoperative blood loss and length of hospital stay for the Endo-TLIF group (60.56 ± 0.36 mL, 8.12 ± 0.92 days, respectively) were statistically significantly lower than those for the MIS-TLIF group (65.47 ± 0.91 mL, 9.66 ± 1.34 days, respectively) (P < 0.05). The VAS and JOA scores of the patients in the two groups at postoperative 1 week, 3 months, 1 year, 2 years (Endo-TLIF VAS: 4.16 ± 0.92, 3.72 ± 1.54, 1.32 ± 0.45, 1.29 ± 0.34; JOA:16.71 ± 0.99, 19.86 ± 0.24, 24.91 ± 0.97, 25.88 ± 0.52; MIS-TLIF VAS: 4.17 ± 1.41, 2.98 ± 0.91, 1.54 ± 0.32, 1.33 ± 0.18; JOA: 16.67 ± 0.67, 19.58 ± 0.65, 25.33 ± 0.73, 25.69 ± 0.33) were statistically significantly improved from the preoperative scores (Endo-TLIF: 8.45 ± 1.44, 14.36 ± 0.56; MIS-TLIF: 8.11 ± 0.93, 14.45 ± 0.34, respectively) (P < 0.01). The VAS and JOA scores of the Endo-TLIF group were statistically significantly better than those of the MIS-TLIF group at 3 months and 1 year after surgery (P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the scores between the two groups at any of the other time points (P > 0.05). There was no significant difference in the intervertebral altitude between the two groups at the 3-month (11.36 ± 0.23, 11.21 ± 0.42, respectively) or final follow-up (10.88 ± 0.64, 10.81 ± 0.39, respectively) (P > 0.05). Dural tears, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, infection, and neurologic injury did not occur. Both groups showed good intervertebral fusion at the last follow-up. The intervertebral fusion rate was 97.5% (39/40) in the Endo-TLIF group and 94.7% (36/38) in the MIS-TLIF group, with no statistically significant difference between the two groups (χ2 = 0.118, P = 0.731). At the final follow-up, the modified MacNab's criteria were 92.5% and 89.5% between the two groups.
Conclusion: Endo-TLIF with percutaneous pedicle screws (PPS) performed by using a visualization system for lumbar degenerative disease may be regarded as an efficient alternative surgery for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. It is a safe and minimally invasive way to perform this surgery and has shown satisfactory clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion; Lumbar spinal stenosis; Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion; Percutaneous pedicle screw (PPS).
© 2021 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Chinese Orthopaedic Association and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures

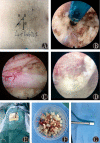
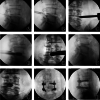
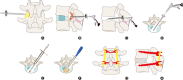
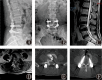
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the short-term efficacy of MIS-TLIF and Endo-LIF for the treatment of two-segment lumbar degenerative disease.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Sep 4;25(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07815-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39232720 Free PMC article.
-
[Two different techniques combined with MIS-TLIF in the treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis:a case-control study].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022 May 25;35(5):409-17. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2022.05.002. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022. PMID: 35535527 Chinese.
-
Comparison of hidden blood loss and clinical efficacy of percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.Int Orthop. 2022 Sep;46(9):2063-2070. doi: 10.1007/s00264-022-05485-z. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Int Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35723702 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2021 Aug;152:e352-e368. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.05.109. Epub 2021 Jun 1. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34087465
-
Comparison of Endoscopic and Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Meta-analysis.Clin Spine Surg. 2024 Mar 1;37(2):56-66. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000001428. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Clin Spine Surg. 2024. PMID: 36727763
Cited by
-
Effect of Tranexamic Acid on Hidden Blood Loss in Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Retrospective Study.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024 May 29;20:325-334. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S462784. eCollection 2024. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2024. PMID: 38827486 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes and Complications Between Endoscopic and Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Global Spine J. 2023 Jun;13(5):1394-1404. doi: 10.1177/21925682221142545. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Global Spine J. 2023. PMID: 36447426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Percutaneous endoscopic versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2022 Dec;17(4):591-600. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2022.118680. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2022. PMID: 36818507 Free PMC article.
-
How to Set Working Cannula in Endoscopic-Assisted Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Morphometric Analysis Based on Computed Tomography.Orthop Surg. 2024 Dec;16(12):3006-3013. doi: 10.1111/os.14239. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 39252538 Free PMC article.
-
Is endoscopic technique an effective and safe alternative for lumbar interbody fusion? A systematic review and meta-analysis.EFORT Open Rev. 2024 Jun 3;9(6):536-555. doi: 10.1530/EOR-23-0167. EFORT Open Rev. 2024. PMID: 38828975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foley KT, Gupta SK, Justis JR, Sherman MC. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine. Neurosurg Focus, 2001, 10: E10. - PubMed
-
- Kim JS, Jung B, Lee SH. Instrumented minimally invasive spinal‐Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS‐TLIF): minimum 5‐year follow‐up with clinical and radiologic outcomes. Clin Spine Surg, 2018, 31: E302–E309. - PubMed
-
- Ozgur BM, Aryan HE, Pimenta L, Taylor WR. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF): a novel surgical technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J, 2006, 6: 435–443. - PubMed
-
- Aryan HE, Newman CB, Gold JJ, Acosta FL Jr, Coover C, Ames CP. Percutaneous axial lumbar interbody fusion (AxiaLIF) of the L5‐S1 segment: initial clinical and radiographic experience. Minim Invasive Neurosurg, 2008, 51: 225–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CY2017-QN12/Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital
- CY2017-ZD02/Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital
- ynbskyjj2015-2-9/Doctoral Research fund of Lanzhou University Second Hospital
- lzujbky-2019-kb16/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- LHGJ20190859/Joint project of Medical science and Technology of Henan Province
- 2018-3-52/Lanzhou Science and Technology Plan Program
- 2017-4-88/Lanzhou Science and Technology Plan Program
- 81874017/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81960403/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 17JR5RA188/Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China
- HWYX 2019159/Overseas Research and Training Project of Health Science and Technology Talents in Henan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

