The Right Temporal Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia Is Not Genetically Sporadic: A Case Series
- PMID: 33427744
- PMCID: PMC7990443
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-201191
The Right Temporal Variant of Frontotemporal Dementia Is Not Genetically Sporadic: A Case Series
Abstract
Background: Right temporal variant frontotemporal dementia (rtvFTD) has been generally considered as a right sided variant of semantic variant primary progressive aphasia (svPPA), which is a genetically sporadic disorder. Recently, we have shown that rtvFTD has a unique clinical syndrome compared to svPPA and behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia.
Objective: We challenge the assumption that rtvFTD is a sporadic, non-familial variant of FTD by identifying potential autosomal dominant inheritance and related genes in rtvFTD.
Methods: We collected all subjects with a diagnosis of FTD or primary progressive aphasia who had undergone genetic screening (n = 284) and subsequently who had a genetic variant (n = 48) with a diagnosis of rtvFTD (n = 6) in 2 specialized memory clinics.
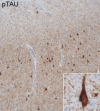
Results: Genetic variants in FTD related genes were found in 33% of genetically screened rtvFTD cases; including MAPT (n = 4), GRN (n = 1), and TARDBP (n = 1) genes, whereas only one svPPA case had a genetic variant in our combined cohorts. Additionally, 4 out of 6 rtvFTD subjects had a strong family history for dementia.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that rtvFTD, unlike svPPA, is not a pure sporadic, but a heterogeneous potential genetic variant of FTD, and screening for genetic causes for FTD should be performed in patients with rtvFTD.
Keywords: Dementia; GRN; MAPT; TARDBP; frontotemporal dementia; frontotemporal lobar degeneration; genetic; right temporallobe.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures
References
-
- Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A, Robert PH, Albert M, Boone K, Miller BL, Cummings J, Benson DF (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: A consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51, 1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Rascovsky K, Hodges JR, Knopman D, Mendez MF, Kramer JH, Neuhaus J, van Swieten JC, Seelaar H, Dopper EG, Onyike CU, Hillis AE, Josephs KA, Boeve BF, Kertesz A, Seeley WW, Rankin KP, Johnson JK, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rosen H, Prioleau-Latham CE, Lee A, Kipps CM, Lillo P, Piguet O, Rohrer JD, Rossor MN, Warren JD, Fox NC, Galasko D, Salmon DP, Black SE, Mesulam M, Weintraub S, Dickerson BC, Diehl-Schmid J, Pasquier F, Deramecourt V, Lebert F, Pijnenburg Y, Chow TW, Manes F, Grafman J, Cappa SF, Freedman M, Grossman M, Miller BL (2011) Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134, 2456–2477. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gorno-Tempini ML, Hillis AE, Weintraub S, Kertesz A, Mendez M, Cappa SF, Ogar JM, Rohrer JD, Black S, Boeve BF, Manes F, Dronkers NF, Vandenberghe R, Rascovsky K, Patterson K, Miller BL, Knopman DS, Hodges JR, Mesulam MM, Grossman M (2011) Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 76, 1006–1014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rohrer JD, Guerreiro R, Vandrovcova J, Uphill J, Reiman D, Beck J, Isaacs AM, Authier A, Ferrari R, Fox NC, Mackenzie IR, Warren JD, de Silva R, Holton J, Revesz T, Hardy J, Mead S, Rossor MN (2009) The heritability and genetics of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurology 73, 1451–1456. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

