Four hub genes regulate tumor infiltration by immune cells, antitumor immunity in the tumor microenvironment, and survival outcomes in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients
- PMID: 33428598
- PMCID: PMC7906216
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202351
Four hub genes regulate tumor infiltration by immune cells, antitumor immunity in the tumor microenvironment, and survival outcomes in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients
Abstract
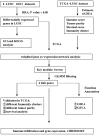
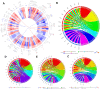
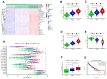
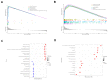
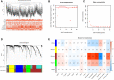
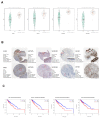
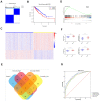
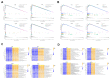
In this study, we performed bioinformatics analyses to identify hub genes that regulate tumor infiltration by immune cells and antitumor immunity in the lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). We identified 1738 robust and stable differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the LUSC tissues based on robust rank aggregation (RRA) analysis of RNA-sequencing data from 5 GEO-LUSC datasets. We then classified TCGA-LUSC patients based on ssGSEA and ESTIMATE analyses of LUSC tissues into high, medium and low immunity subgroups showing significant differences in tumor purity. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of the robust DEGs revealed five immunity-related modules, including the brown module with 762 DEGs and 30 hub genes showing the highest correlation with the immunity-related LUSC patient subgroups and their clinicopathological characteristics. We selected four hub genes, LAPTM5, C1QC, CSF1R and SLCO2B1, for validation of the immunity status and prognosis of LUSC patients. High expression of these four genes correlated with increased infiltration of immune cell types, upregulation of the immunosuppressive TOX pathway genes, CD8+ T cell exhaustion, and shorter overall survival of LUSC patients. These findings demonstrate that four hub genes regulate tumor infiltration of immune cells, anti-tumor immunity, and survival outcomes in LUSC patients.
Keywords: CIBERSORT; immunity; lung squamous carcinoma; robust rank aggregations; single sample gene set enrichment analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lysosomal transmembrane protein 5: Impact on immune cell function and implications for immune-related deficiencies.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36705. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36705. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A robust signature associated with patient prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment based on immune-related genes in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106856. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106856. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32777677
-
Significance of NKX2-1 as a biomarker for clinical prognosis, immune infiltration, and drug therapy in lung squamous cell carcinoma.PeerJ. 2024 May 1;12:e17338. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17338. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38708353 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Infiltration Landscape in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Implications.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 10;2020:5981870. doi: 10.1155/2020/5981870. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33102584 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in preclinical models for lung squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogene. 2021 Apr;40(16):2817-2829. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01723-7. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33707749 Review.
Cited by
-
C1QC is a prognostic biomarker with immune-related value in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 13;14:1109991. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1109991. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36992705 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal transmembrane protein 5: Impact on immune cell function and implications for immune-related deficiencies.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36705. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36705. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
POLR1A inhibits ferroptosis by regulating TFAM-mediated mitophagy and iron homeostasis.Redox Biol. 2025 Jul 8;85:103758. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103758. Online ahead of print. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40669210 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-scale integrative analyses identify THBS2+ cancer-associated fibroblasts as a key orchestrator promoting aggressiveness in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.Theranostics. 2022 Mar 28;12(7):3104-3130. doi: 10.7150/thno.69590. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35547750 Free PMC article.
-
Application of weighted co-expression network analysis and machine learning to identify the pathological mechanism of Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 13;14:837770. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.837770. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35912089 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

