Efficient induction of pancreatic alpha cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells by controlling the timing for BMP antagonism and activation of retinoic acid signaling
- PMID: 33428669
- PMCID: PMC7799802
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245204
Efficient induction of pancreatic alpha cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells by controlling the timing for BMP antagonism and activation of retinoic acid signaling
Abstract
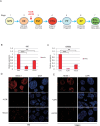
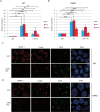
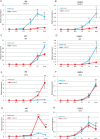
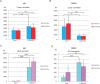
Diabetes mellitus is caused by breakdown of blood glucose homeostasis, which is maintained by an exquisite balance between insulin and glucagon produced respectively by pancreatic beta cells and alpha cells. However, little is known about the mechanism of inducing glucagon secretion from human alpha cells. Many methods for generating pancreatic beta cells from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have been reported, but only two papers have reported generation of pancreatic alpha cells from hPSCs. Because NKX6.1 has been suggested as a very important gene for determining cell fate between pancreatic beta and alpha cells, we searched for the factors affecting expression of NKX6.1 in our beta cell differentiation protocols. We found that BMP antagonism and activation of retinoic acid signaling at stage 2 (from definitive endoderm to primitive gut tube) effectively suppressed NKX6.1 expression at later stages. Using two different hPSCs lines, treatment with BMP signaling inhibitor (LDN193189) and retinoic acid agonist (EC23) at Stage 2 reduced NKX6.1 expression and allowed differentiation of almost all cells into pancreatic alpha cells in vivo after transplantation under a kidney capsule. Our study demonstrated that the cell fate of pancreatic cells can be controlled by adjusting the expression level of NKX6.1 with proper timing of BMP antagonism and activation of retinoic acid signaling during the pancreatic differentiation process. Our method is useful for efficient induction of pancreatic alpha cells from hPSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficient generation of functional pancreatic β-cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells.J Diabetes. 2017 Feb;9(2):168-179. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12400. Epub 2016 May 31. J Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 27038181
-
Enhanced differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into pancreatic progenitors co-expressing PDX1 and NKX6.1.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jan 23;9(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0759-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29361979 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Endoderm-Derived From Diabetic Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Generates Glucose-Responsive Insulin-Secreting Cells.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Oct;232(10):2616-2625. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25459. Epub 2016 Dec 29. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27306424
-
Redefining the signaling pathways from pluripotency to pancreas development: In vitro β-cell differentiation.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):7811-7827. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27736. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30480819 Review.
-
Growth factor signalling in the regulation of α-cell fate.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Oct;13 Suppl 1:21-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01442.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21824253 Review.
Cited by
-
GLP-1 Analogue-Loaded Glucose-Responsive Nanoparticles as Allies of Stem Cell Therapies for the Treatment of Type I Diabetes.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 May 2;7(5):1650-1663. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00173. eCollection 2024 May 10. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38751616 Free PMC article.
-
Human pancreatic microenvironment promotes β-cell differentiation via non-canonical WNT5A/JNK and BMP signaling.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 12;13(1):1952. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29646-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35414140 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

