YAP1 and its fusion proteins in cancer initiation, progression and therapeutic resistance
- PMID: 33428889
- PMCID: PMC8107117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.12.018
YAP1 and its fusion proteins in cancer initiation, progression and therapeutic resistance
Abstract
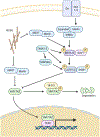
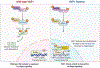
YAP1 is a transcriptional co-activator whose activity is controlled by the Hippo signaling pathway. In addition to important functions in normal tissue homeostasis and regeneration, YAP1 has also prominent functions in cancer initiation, aggressiveness, metastasis, and therapy resistance. In this review we are discussing the molecular functions of YAP1 and its roles in cancer, with a focus on the different mechanisms of de-regulation of YAP1 activity in human cancers, including inactivation of upstream Hippo pathway tumor suppressors, regulation by intersecting pathways, miRNAs, and viral oncogenes. We are also discussing new findings on the function and biology of the recently identified family of YAP1 gene fusions, that constitute a new type of activating mutation of YAP1 and that are the likely oncogenic drivers in several subtypes of human cancers. Lastly, we also discuss different strategies of therapeutic inhibition of YAP1 functions.
Keywords: Cancer; Gene fusions; Hippo signaling pathway; YAP1; YAP1 fusion.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ahronowitz I, Xin W, Kiely R, Sims K, MacCollin M, Nunes FP. 2007. Mutational spectrum of the NF2 gene: a meta-analysis of 12 years of research and diagnostic laboratory findings. Hum Mutat 28: 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, Piccolo S. 2013. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell 154: 1047–1059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

