lnc-Rps4l-encoded peptide RPS4XL regulates RPS6 phosphorylation and inhibits the proliferation of PASMCs caused by hypoxia
- PMID: 33429084
- PMCID: PMC8058491
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.01.005
lnc-Rps4l-encoded peptide RPS4XL regulates RPS6 phosphorylation and inhibits the proliferation of PASMCs caused by hypoxia
Erratum in
-
lnc-Rps4l-encoded peptide RPS4XL regulates RPS6 phosphorylation and inhibits the proliferation of PASMCs caused by hypoxia.Mol Ther. 2024 Aug 7;32(8):2799. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.06.032. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38959895 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
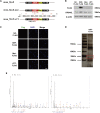
Pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) proliferation caused by hypoxia is an important pathological process of pulmonary hypertension (PH). Prevention of PASMCs proliferation can effectively reduce PH mortality. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the proliferation process. Recent evidence has demonstrated that functional peptides encoded by lncRNAs play important roles in cell pathophysiological process. Our previous study has demonstrated that lnc-Rps4l with high coding ability mediates the PASMCs proliferation under hypoxic conditions. We hypothesize in this study that a lnc-Rps4l-encoded peptide is involved in hypoxic-induced PASMCs proliferation. The presence of peptide 40S ribosomal protein S4 X isoform-like (RPS4XL) encoded by lnc-Rps4l in PASMCs under hypoxic conditions was confirmed by bioinformatics, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Inhibition of proliferation by the peptide RPS4XL was demonstrated in hypoxic PASMCs by MTT, bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation, and immunofluorescence assays. By using the bioinformatics, coimmunoprecipitation (coIP), and mass spectrometry, RPS6 was identified to interact with RPS4XL. Furthermore, lnc-Rps4l-encoded peptide RPS4XL inhibited the RPS6 process via binding to RPS6 and inhibiting RPS6 phosphorylation at p-RPS6 (Ser240+Ser244) phosphorylation site. These results systematically elucidate the role and regulatory network of Rps4l-encoded peptide RPS4XL in PASMCs proliferation. These discoveries provide potential targets for early diagnosis and a leading compound for treatment of hypoxic PH.
Keywords: Rps4l-encoded conserved peptide RPS4XL; hypoxia; long non-coding RNA Rps4l; proliferation; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Copyright © 2021 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Boucly A., Morélot-Panzini C., Garcia G., Weatherald J., Jaïs X., Savale L., Montani D., Humbert M., Similowski T., Sitbon O., Laveneziana P. Intensity and quality of exertional dyspnoea in patients with stable pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2020;55:1802108. - PubMed
-
- Frumkin L.R. The pharmacological treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012;64:583–620. - PubMed
-
- Deboeck G., Niset G., Lamotte M., Vachiéry J.L., Naeije R. Exercise testing in pulmonary arterial hypertension and in chronic heart failure. Eur. Respir. J. 2004;23:747–751. - PubMed
-
- Robalino B.D., Moodie D.S. Association between primary pulmonary hypertension and portal hypertension: analysis of its pathophysiology and clinical, laboratory and hemodynamic manifestations. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991;17:492–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

