Process of Obtaining Social Consensus and 3-Year Functional Outcomes of the First Hand Allotransplantation in Korea
- PMID: 33429470
- PMCID: PMC7801147
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e6
Process of Obtaining Social Consensus and 3-Year Functional Outcomes of the First Hand Allotransplantation in Korea
Abstract
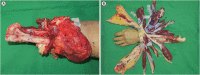
Background: On February 2, 2017, the surgical team of ten board-certified hand specialists of W Hospital in Korea successfully performed the nation's first hand transplantation at Yeungnam University Medical Center (YUMC). This paper reports on the legal, financial, and cultural hurdles that were overcome to open the way for hand transplantation and its functional outcomes at 36 months after the operation.
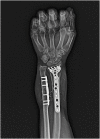
Methods: W Hospital formed a memorandum of understanding with Daegu city and YUMC to comply with government regulations regarding hand transplantation. Campaigns were initiated in the media to increase public awareness and understanding. With the city's financial and legal support and the university's medical cooperation, a surgical team performed a left distal forearm hand transplantation from a brain-dead 48-year-old man to a 35-year-old left-handed man.
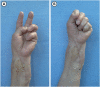
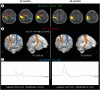
Results: With this successful allotransplantation, the Korean Act on Organ Transplantation has now been amended to include hand transplantation. Korean national health insurance has also begun covering hand transplantation. Functional outcome at 36 months after the operation showed satisfactory progress in both motor and sensory functions. The disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand score were 23. The final Hand Transplantation Score was 90 points. Functional brain magnetic resonance imaging shows significant cortical reorganization of the corticospinal tract, and reinnervation of intrinsic muscle is observed.
Conclusions: Hand transplantation at the distal forearm shows very satisfactory outcomes in functional, aesthetical, and psychological aspects. Legal and financial barriers against hand transplantation have long been the most burdensome issues. Despite this momentous success, there have been no other clinical applications of vascularized composite allotransplantation due to the limited acceptance by Korean doctors and people. Further public education campaigns for vascularized composite allotransplantation are needed to increase awareness and acceptance.
Keywords: Functional Outcome; Hand Transplantation; Korea; Social Consensus.
© 2021 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reaching New Heights: A Comprehensive Study of Hand Transplantations in Korea after Institutionalization of Hand Transplantation Law.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Feb;65(2):108-119. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0365. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 38288651 Free PMC article.
-
One Year Experience of the Hand Allotransplantation First Performed after Korea Organ Transplantation Act (KOTA) Amendment.Arch Plast Surg. 2023 Aug 2;50(4):415-421. doi: 10.1055/a-2059-5570. eCollection 2023 Jul. Arch Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37564718 Free PMC article.
-
The First Hand Allotransplantation in Taiwan: A Report at 9 Months.Ann Plast Surg. 2016 Feb;77 Suppl 1:S12-5. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000758. Ann Plast Surg. 2016. PMID: 26914350
-
Building a Hand and Upper Extremity Transplantation Program: Lessons Learned From the First 20 Years of Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation.Hand (N Y). 2020 Mar;15(2):224-233. doi: 10.1177/1558944718790579. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Hand (N Y). 2020. PMID: 30060684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technology and vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA)-lessons learned from the first bilateral pediatric hand transplant.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016 Nov;27(11):161. doi: 10.1007/s10856-016-5771-9. Epub 2016 Sep 16. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016. PMID: 27638100 Review.
Cited by
-
Reaching New Heights: A Comprehensive Study of Hand Transplantations in Korea after Institutionalization of Hand Transplantation Law.Yonsei Med J. 2024 Feb;65(2):108-119. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2023.0365. Yonsei Med J. 2024. PMID: 38288651 Free PMC article.
-
One Year Experience of the Hand Allotransplantation First Performed after Korea Organ Transplantation Act (KOTA) Amendment.Arch Plast Surg. 2023 Aug 2;50(4):415-421. doi: 10.1055/a-2059-5570. eCollection 2023 Jul. Arch Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37564718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones JW, Gruber SA, Barker JH, Breidenbach WC. Successful hand transplantation. One-year follow-up. Louisville Hand Transplant Team. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(7):468–473. - PubMed
-
- Shores JT, Brandacher G, Lee WP. Hand and upper extremity transplantation: an update of outcomes in the worldwide experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(2):351e–360e. - PubMed
-
- Breidenbach WC, Meister EA, Becker GW, Turker T, Gorantla VS, Hassan K, et al. A statistical comparative assessment of face and hand transplantation outcomes to determine whether either meets the standard of care threshold. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(1):214e–222e. - PubMed
-
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. A proposed rule by the Health and Human Services Department on 12/16/2011. [Updated 2011]. [Accessed June 15, 2017]. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2011/12/16/2011-2204/organ-pro....
-
- Thuong M, Petruzzo P, Landin L, Mahillo B, Kay S, Testelin S, et al. Vascularized composite allotransplantation - a Council of Europe position paper. Transpl Int. 2019;32(3):233–240. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

