Effect of sodium-dependent glucose transporter inhibitors on glycated hemoglobin A1c after 24 weeks in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33429775
- PMCID: PMC7793358
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024101
Effect of sodium-dependent glucose transporter inhibitors on glycated hemoglobin A1c after 24 weeks in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
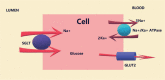
Background: To evaluate dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, empagliflozin, ertugliflozin, and sotagliflozin according to their effect on the glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: The Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and Clinical Trials databases were electronically searched to collect randomized controlled trials of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus through June 2020. Two researchers independently screened and evaluated the obtained studies and extracted the outcome indexes. RevMan 5.3 software was used to perform the meta-analysis and to create plots.
Results: Finally, 27 studies were selected and included in this study. The meta-analysis results showed that sodium-dependent glucose transporter (SGLT) inhibitors significantly reduced the HbA1c level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, these results were highly heterogeneous, so we conducted a subgroup analysis. The results of the subgroup analysis suggested that by dividing populations into different subgroups, the heterogeneity of each group could be reduced.
Conclusions: SGLT inhibitors had a good effect on the HbA1c level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, but there might be differences in the efficacy of SGLT inhibitors in different populations. It is hoped that more studies will be conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SGLT inhibitors in different populations.
Registration number: CRD42020185025.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Cooke DW, Plotnick L. Type 1 diabetes mellitus in pediatrics. Pediatr Rev 2008;29:374–85. - PubMed
-
- Picot J, Jones J, Colquitt JL, et al. The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric (weight loss) surgery for obesity: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2009;13:1-190, 215-357, iii-iv. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

