Improvement Effect of Metformin on Female and Male Reproduction in Endocrine Pathologies and Its Mechanisms
- PMID: 33429918
- PMCID: PMC7826885
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14010042
Improvement Effect of Metformin on Female and Male Reproduction in Endocrine Pathologies and Its Mechanisms
Abstract
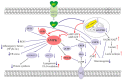
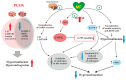
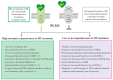
Metformin (MF), a first-line drug to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), alone and in combination with other drugs, restores the ovarian function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and improves fetal development, pregnancy outcomes and offspring health in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and T2DM. MF treatment is demonstrated to improve the efficiency of in vitro fertilization and is considered a supplementary drug in assisted reproductive technologies. MF administration shows positive effect on steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in men with metabolic disorders, thus MF treatment indicates prospective use for improvement of male reproductive functions and fertility. MF lacks teratogenic effects and has positive health effect in newborns. The review is focused on use of MF therapy for restoration of female and male reproductive functions and improvement of pregnancy outcomes in metabolic and endocrine disorders. The mechanisms of MF action are discussed, including normalization of metabolic and hormonal status in PCOS, GDM, T2DM and metabolic syndrome and restoration of functional activity and hormonal regulation of the gonadal axis.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; folliculogenesis; gestational diabetes mellitus; gonadotropin; in vitro fertilization; insulin; metformin; ovary; polycystic ovary syndrome; steroidogenesis; testes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Madsen K.S., Chi Y., Metzendorf M.I., Richter B., Hemmingsen B. Metformin for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in persons at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019;12:CD008558. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008558.pub2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lavine J.E., Schwimmer J.B., Van Natta M.L., Molleston J.P., Murray K.F., Rosenthal P., Abrams S.H., Scheimann A.O., Sanyal A.J., Chalasani N., et al. Effect of vitamin E or metformin for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: The TONIC randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2011;305:1659–1668. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.520. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohan M., Al-Talabany S., McKinnie A., Mordi I.R., Singh J.S.S., Gandy S.J., Baig F., Hussain M.S., Bhalraam U., Khan F., et al. A randomized controlled trial of metformin on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with coronary artery disease without diabetes: The MET-REMODEL trial. Eur. Heart J. 2019;40:3409–3417. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz203. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

