Nitric Oxide and S-Nitrosylation in Cardiac Regulation: G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase-2 and β-Arrestins as Targets
- PMID: 33430208
- PMCID: PMC7825736
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020521
Nitric Oxide and S-Nitrosylation in Cardiac Regulation: G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase-2 and β-Arrestins as Targets
Abstract
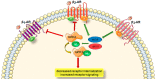
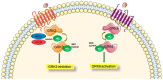
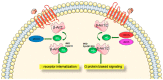
Cardiac diseases including heart failure (HF), are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally. Among the prominent characteristics of HF is the loss of β-adrenoceptor (AR)-mediated inotropic reserve. This is primarily due to the derangements in myocardial regulatory signaling proteins, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinases (GRKs) and β-arrestins (β-Arr) that modulate β-AR signal termination via receptor desensitization and downregulation. GRK2 and β-Arr2 activities are elevated in the heart after injury/stress and participate in HF through receptor inactivation. These GPCR regulators are modulated profoundly by nitric oxide (NO) produced by NO synthase (NOS) enzymes through S-nitrosylation due to receptor-coupled NO generation. S-nitrosylation, which is NO-mediated modification of protein cysteine residues to generate an S-nitrosothiol (SNO), mediates many effects of NO independently from its canonical guanylyl cyclase/cGMP/protein kinase G signaling. Herein, we review the knowledge on the NO system in the heart and S-nitrosylation-dependent modifications of myocardial GPCR signaling components GRKs and β-Arrs.
Keywords: GRK2; S-nitrosylation; nitric oxide; β-arrestins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor signaling by S-nitrosylation of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2.Cell. 2007 May 4;129(3):511-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.046. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17482545
-
Convergence of G protein-coupled receptor and S-nitrosylation signaling determines the outcome to cardiac ischemic injury.Sci Signal. 2013 Oct 29;6(299):ra95. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004225. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24170934 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular signaling through G protein-coupled receptors: new concepts.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009 Mar;18(2):153-9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283252efe. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19434053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis by G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2; The role of NADPH oxidase 4.Cell Signal. 2016 Mar;28(3):190-203. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.11.013. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 26631573 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinases in normal and failing myocardium.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jun 1;16(8):3047-60. doi: 10.2741/3898. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21622221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial Dysfunction in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: What are the Experimental Proofs?Front Physiol. 2022 Jul 8;13:906272. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.906272. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35874523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted nature of SUMOylation in heart disease and its therapeutic potential.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Aug;480(8):4725-4743. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05286-z. Epub 2025 Apr 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40287894 Review.
-
G Protein-Coupled Receptor and Their Kinases in Cell Biology and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 14;23(10):5501. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105501. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628313 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus nephritis serum induces changes in gene expression in human glomerular endothelial cells, which is modulated by L-sepiapterin: implications for redox-mediated endothelial dysfunction.Lupus Sci Med. 2025 Jun 5;12(1):e001568. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2025-001568. Lupus Sci Med. 2025. PMID: 40480647 Free PMC article.
-
A new look at the role of nitric oxide in preeclampsia: Protein S-nitrosylation.Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022 Aug;29:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2022.05.008. Epub 2022 May 27. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35660510 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

