Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain for Securing the Edge Internet of Things
- PMID: 33430274
- PMCID: PMC7825674
- DOI: 10.3390/s21020359
Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain for Securing the Edge Internet of Things
Abstract
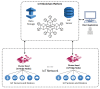
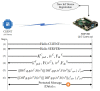
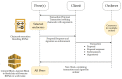
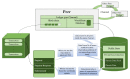
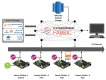
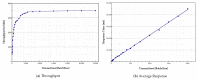
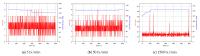
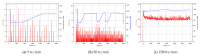
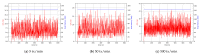
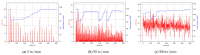
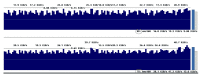
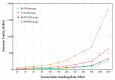
Providing security and privacy to the Internet of Things (IoT) networks while achieving it with minimum performance requirements is an open research challenge. Blockchain technology, as a distributed and decentralized ledger, is a potential solution to tackle the limitations of the current peer-to-peer IoT networks. This paper presents the development of an integrated IoT system implementing the permissioned blockchain Hyperledger Fabric (HLF) to secure the edge computing devices by employing a local authentication process. In addition, the proposed model provides traceability for the data generated by the IoT devices. The presented solution also addresses the IoT systems' scalability challenges, the processing power and storage issues of the IoT edge devices in the blockchain network. A set of built-in queries is leveraged by smart-contracts technology to define the rules and conditions. The paper validates the performance of the proposed model with practical implementation by measuring performance metrics such as transaction throughput and latency, resource consumption, and network use. The results show that the proposed platform with the HLF implementation is promising for the security of resource-constrained IoT devices and is scalable for deployment in various IoT scenarios.
Keywords: Internet of Things; data provenance; edge computing; hyperledger fabric; security and privacy; smart contract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Experimental Performance Analysis of a Scalable Distributed Hyperledger Fabric for a Large-Scale IoT Testbed.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 28;22(13):4868. doi: 10.3390/s22134868. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808363 Free PMC article.
-
A secure end-to-end communication framework for cooperative IoT networks using hybrid blockchain system.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 1;15(1):11077. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96002-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40169696 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Layer Blockchain-Based Security Architecture for Internet of Things.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 24;21(3):772. doi: 10.3390/s21030772. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498860 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Comparison between the Ethereum and Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain Platforms for Attribute-Based Access Control in Smart Home IoT Environments.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 9;23(16):7046. doi: 10.3390/s23167046. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging Blockchain Technology for Ensuring Security and Privacy Aspects in Internet of Things: A Systematic Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;23(2):788. doi: 10.3390/s23020788. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a Secure and Scalable Maritime Monitoring System Using Blockchain and Low-Cost IoT Technology.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;22(13):4895. doi: 10.3390/s22134895. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808390 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging a novel NFT-enabled blockchain architecture for the authentication of IoT assets in smart cities.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 13;13(1):19785. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45212-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37957161 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Correlation between Temperature of IoT Microcontroller Devices and Blockchain Energy Consumption in Wireless Sensor Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 10;23(14):6265. doi: 10.3390/s23146265. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514560 Free PMC article.
-
An Analysis of Blockchain-Based IoT Sensor Network Distributed Denial of Service Attacks.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 12;24(10):3083. doi: 10.3390/s24103083. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793937 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Performance Optimization and Application in Smart Home for Hyperledger Fabric.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 22;22(9):3222. doi: 10.3390/s22093222. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35590909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali M.S., Vecchio M., Pincheira M., Dolui K., Antonelli F., Rehmani M.H. Applications of blockchains in the Internet of Things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018;21:1676–1717. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2886932. - DOI
-
- Lao L., Li Z., Hou S., Xiao B., Guo S., Yang Y. A survey of IoT applications in blockchain systems: Architecture, consensus, and traffic modeling. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2020;53:1–32. doi: 10.1145/3372136. - DOI
-
- Javaid U., Siang A.K., Aman M.N., Sikdar B. Mitigating loT device based DDoS attacks using blockchain; Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Cryptocurrencies and Blockchains for Distributed Systems; Munich, Germany. 15 June 2018; pp. 71–76.
-
- Zhou X., Tang X. Research and implementation of RSA algorithm for encryption and decryption; Proceedings of the 2011 6th International Forum on Strategic Technology; Harbin, China. 22–24 August 2011; pp. 1118–1121.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

