Associations between Statin/Omega3 Usage and MRI-Based Radiomics Signatures in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 33430275
- PMCID: PMC7825695
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11010085
Associations between Statin/Omega3 Usage and MRI-Based Radiomics Signatures in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
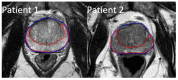
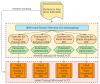
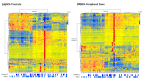
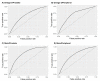
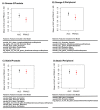
Prostate cancer is the most common noncutaneous cancer and the second leading cause of cancer deaths among American men. Statins and omega-3 are two medications recently found to correlate with prostate cancer risk and aggressiveness, but the observed associations are complex and controversial. We therefore explore the novel application of radiomics in studying statin and omega-3 usage in prostate cancer patients. On MRIs of 91 prostate cancer patients, two regions of interest (ROIs), the whole prostate and the peripheral region of the prostate, were manually segmented. From each ROI, 944 radiomic features were extracted after field bias correction and normalization. Heatmaps were generated to study the radiomic feature patterns against statin or omega-3 usage. Radiomics models were trained on selected features and evaluated with 500-round threefold cross-validation for each drug/ROI combination. On the 1500 validation datasets, the radiomics model achieved average AUCs of 0.70, 0.74, 0.78, and 0.72 for omega-3/prostate, omega-3/peripheral, statin/prostate, and statin/peripheral, respectively. As the first study to analyze radiomics in relation to statin and omega-3 uses in prostate cancer patients, our study preliminarily established the existence of imaging-identifiable tissue-level changes in the prostate and illustrated the potential usefulness of radiomics for further exploring these medications' effects and mechanisms in prostate cancer.
Keywords: MRI; artificial intelligence; omega-3; prostate cancer; radiomics; statin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T2w-MRI signal normalization affects radiomics features reproducibility.Med Phys. 2020 Apr;47(4):1680-1691. doi: 10.1002/mp.14038. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 31971614
-
Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Characterization: Combined Use of Radiomics Model with PI-RADS and Clinical Parameters.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 2;12(7):1767. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071767. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630787 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease Diagnosis Using Neostriatum Radiomic Features Based on T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Front Neurol. 2020 Apr 8;11:248. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00248. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32322236 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate MRI radiomics: A systematic review and radiomic quality score assessment.Eur J Radiol. 2020 Aug;129:109095. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109095. Epub 2020 May 30. Eur J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32531722
-
Evidence on Statins, Omega-3, and Prostate Cancer: A Narrative Review.World J Mens Health. 2022 Jul;40(3):412-424. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.210139. Epub 2022 Jan 1. World J Mens Health. 2022. PMID: 35021299 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of MRI-Derived Radiomic Models in Prostate Cancer Risk Stratification: A Critical Review of Contemporary Literature.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;13(6):1128. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13061128. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measuring the bias of incorrect application of feature selection when using cross-validation in radiomics.Insights Imaging. 2021 Nov 24;12(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13244-021-01115-1. Insights Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34817740 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary attempt to use radiomic features in the diagnosis of extra-articular long head biceps tendinitis.MAGMA. 2023 Aug;36(4):651-658. doi: 10.1007/s10334-022-01050-2. Epub 2022 Nov 30. MAGMA. 2023. PMID: 36449124
-
A Novel Application of Unsupervised Machine Learning and Supervised Machine Learning-Derived Radiomics in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021 Jun 23;14:2657-2664. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S312330. eCollection 2021. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021. PMID: 34188576 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Prostate Cancer Disease Aggressiveness Using Bi-Parametric Mri Radiomics.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 1;13(23):6065. doi: 10.3390/cancers13236065. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gevariya N., Besancon M., Robitaille K., Picard V., Diabaté L., Alesawi A., Julien P., Fradet Y., Bergeron A., Fradet V., et al. Omega-3 fatty acids decrease prostate cancer progression 0.586associated with an anti-tumor immune response in eugonadal and castrated mice. Prostate. 2019;79:9–20. doi: 10.1002/pros.23706. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

