Mapping the SARS-CoV-2-Host Protein-Protein Interactome by Affinity Purification Mass Spectrometry and Proximity-Dependent Biotin Labeling: A Rational and Straightforward Route to Discover Host-Directed Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics
- PMID: 33430309
- PMCID: PMC7825748
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020532
Mapping the SARS-CoV-2-Host Protein-Protein Interactome by Affinity Purification Mass Spectrometry and Proximity-Dependent Biotin Labeling: A Rational and Straightforward Route to Discover Host-Directed Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics
Abstract
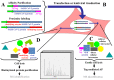
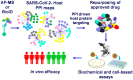
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are the vital engine of cellular machinery. After virus entry in host cells the global organization of the viral life cycle is strongly regulated by the formation of virus-host protein interactions. With the advent of high-throughput -omics platforms, the mirage to obtain a "high resolution" view of virus-host interactions has come true. In fact, the rapidly expanding approaches of mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics in the study of PPIs provide efficient tools to identify a significant number of potential drug targets. Generation of PPIs maps by affinity purification-MS and by the more recent proximity labeling-MS may help to uncover cellular processes hijacked and/or altered by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), providing promising therapeutic targets. The possibility to further validate putative key targets from high-confidence interactions between viral bait and host protein through follow-up MS-based multi-omics experiments offers an unprecedented opportunity in the drug discovery pipeline. In particular, drug repurposing, making use of already existing approved drugs directly targeting these identified and validated host interactors, might shorten the time and reduce the costs in comparison to the traditional drug discovery process. This route might be promising for finding effective antiviral therapeutic options providing a turning point in the fight against the coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) outbreak.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; affinity-purification mass spectrometry; antiviral; drug repurposing; emerging; protein–protein interaction; proteomics; proximity-dependent biotin labeling (BioID); virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contributions of human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in determining host-pathogen interaction of COVID-19.J Genet. 2021;100(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12041-021-01262-w. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 33707363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repositioning of histamine H1 receptor antagonist: Doxepin inhibits viropexis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike pseudovirus by blocking ACE2.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 5;896:173897. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173897. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33497607 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein/ACE2 Protein-Protein Interactions: a Computational Study.Mol Inform. 2021 Jun;40(6):e2060080. doi: 10.1002/minf.202060080. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Mol Inform. 2021. PMID: 33904240 Free PMC article.
-
The Repurposed ACE2 Inhibitors: SARS-CoV-2 Entry Blockers of Covid-19.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021 Oct 8;379(6):40. doi: 10.1007/s41061-021-00353-7. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021. PMID: 34623536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2-host proteome interactions for antiviral drug discovery.Mol Syst Biol. 2021 Nov;17(11):e10396. doi: 10.15252/msb.202110396. Mol Syst Biol. 2021. PMID: 34709727 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tissue- and cell-expression of druggable host proteins provide insights into repurposing drugs for COVID-19.Clin Transl Sci. 2022 Dec;15(12):2796-2811. doi: 10.1111/cts.13400. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Clin Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36259251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in PROTAC-Based Antiviral Strategies.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;11(2):270. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020270. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of PROTACs: a promising drug discovery paradigm.Mol Biomed. 2022 Dec 20;3(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s43556-022-00112-0. Mol Biomed. 2022. PMID: 36536188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of Catecholamine Biosynthetic/Metabolic Pathway in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity.Cells. 2022 Dec 20;12(1):12. doi: 10.3390/cells12010012. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611805 Free PMC article.
-
Combating pan-coronavirus infection by indomethacin through simultaneously inhibiting viral replication and inflammatory response.iScience. 2023 Aug 16;26(9):107631. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107631. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37664584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

