"Girls Aren't Meant to Exercise": Perceived Influences on Physical Activity among Adolescent Girls-The HERizon Project
- PMID: 33430413
- PMCID: PMC7827342
- DOI: 10.3390/children8010031
"Girls Aren't Meant to Exercise": Perceived Influences on Physical Activity among Adolescent Girls-The HERizon Project
Abstract
Background: Adolescent girls are less active than boys, with approximately 10% of girls in Ireland and the United Kingdom meeting the minimum recommended daily physical activity (PA) guidelines. This study investigated factors perceived to influence PA among adolescent girls from low socioeconomic areas in order to inform the design of a future intervention (The HERizon Project).
Methods: A total of 48 adolescent girls (13-18 years) from low socioeconomic areas of the United Kingdom and Ireland participated in focus groups (n = 8), to explore perspectives of physical activity and the influence of gender within this. Focus groups were thematically analyzed and interpreted within a socioecological framework.
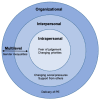
Results: Most girls enjoyed PA and were aware of its benefits. They identified both barriers and facilitators to PA at intrapersonal (fear of judgement and changing priorities WITH age), interpersonal (changing social pressures and support from others) and organizational (delivery of PE) levels. Gender inequality was a multilevel factor, crossing all socioecological levels.
Conclusion: Although many adolescent girls enjoy PA, their experiences appear to be limited by a fear of judgement and an overarching sense of gender inequality. Future interventions, such as the HERizon Project, should address influences at intrapersonal, interpersonal and organizational levels to promote positive PA experiences for adolescent girls.
Keywords: adolescence; exercise; focus groups; girls; physical activity; qualitative; socioecological model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cristi-Montero C., Chillon P., Labayen I., Casajus J., Gonzalez-Gross M., Vanhelst J., Manios Y., Moreno L., Oretga F., Ruiz J. HELENA study group, Caridometabolic risk through an integrative classification combining physical activity and sedentary behaviour in European adolescents: HELENA study. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019;8:55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2018.03.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biddle S., Ciaccioni S., Thomas G., Vergeer I. Physical activity and mental health in children and adolescents: An updated review of reviews and an analysis of causality. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2019;42:146–155. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2018.08.011. - DOI
-
- Kieszczewska D., Szkutnik A., Siedlecka J., Mazur J. Physical activity, sedentary behaviours and duration of sleep as factors affecting the well-being of young people against the background of environmental moderators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019;16:915. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16060915. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical