Inactivation of Material from SARS-CoV-2-Infected Primary Airway Epithelial Cell Cultures
- PMID: 33430421
- PMCID: PMC7839057
- DOI: 10.3390/mps4010007
Inactivation of Material from SARS-CoV-2-Infected Primary Airway Epithelial Cell Cultures
Abstract
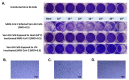
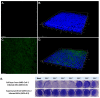
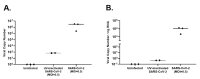
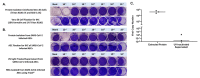
Given that the airway epithelium is the initial site of infection, study of primary human airway epithelial cells (AEC) infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) will be crucial to improved understanding of viral entry factors and innate immune responses to the virus. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidance recommends work with live SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture be conducted in a Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) laboratory. To facilitate downstream assays of materials from experiments there is a need for validated protocols for SARS-CoV-2 inactivation to facilitate safe transfer of material out of a BSL-3 laboratory. We propagated stocks of SARS-CoV-2, then evaluated the effectiveness of heat (65 °C) or ultraviolet (UV) light inactivation. We infected differentiated human primary AECs with SARS-CoV-2, then tested protocols designed to inactivate SARS-CoV-2 in supernatant, protein isolate, RNA, and cells fixed for immunohistochemistry by exposing Vero E6 cells to materials isolated/treated using these protocols. Heating to 65 °C for 10 min or exposing to UV light fully inactivated SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, we found in SARS-CoV-2-infected primary AEC cultures that treatment of supernatant with UV light, isolation of RNA with Trizol®, isolation of protein using a protocol including sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) 0.1% and Triton X100 1%, and fixation of AECs using 10% formalin and Triton X100 1%, each fully inactivated SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; RNA; SARS-CoV-2; Vero E6; airway; epithelial; heat; inactivation; protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus Resource Center Mortality Analyses. [(accessed on 24 December 2020)]; Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/data/mortality.
-
- Lai C.C., Liu Y.H., Wang C.Y., Wang Y.H., Hsueh S.C., Yen M.Y., Ko W.C., Hsueh P.R. Asymptomatic carrier state, acute respiratory disease, and pneumonia due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Facts and myths. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020;53:404–412. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

