mRNA and miRNA Expression Analyses of the MYC/ E2F/miR-17-92 Network in the Most Common Pediatric Brain Tumors
- PMID: 33430425
- PMCID: PMC7827072
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22020543
mRNA and miRNA Expression Analyses of the MYC/ E2F/miR-17-92 Network in the Most Common Pediatric Brain Tumors
Abstract
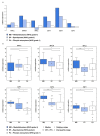
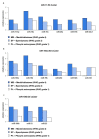
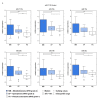
Numerous molecular factors disrupt the correctness of the cell cycle process leading to the development of cancer due to increased cell proliferation. Among known causative factors of such process is abnormal gene expression. Nowadays in the light of current knowledge such alterations are frequently considered in the context of mRNA-miRNA correlation. One of the molecular factors with potential value in tumorigenesis is the feedback loop between MYC and E2F genes in which miR-17-5p and miR-20a from the miR-17-92 cluster are involved. The current literature shows that overexpression of the members of the OncomiR-1 are involved in the development of many solid tumors. In the present work, we investigated the expression of components of the MYC/E2F/miR-17-92 network and their closely related elements including members of MYC and E2F families and miRNAs from two paralogs of miR-17-92: miR-106b-25 and miR-106a-363, in the most common brain tumors of childhood, pilocytic astrocytoma (PA), WHO grade 1; ependymoma (EP), WHO grade 2; and medulloblastoma (MB), WHO grade 4. We showed that the highest gene expression was observed in the MYC family for MYCN and in the E2F family for E2F2. Positive correlation was observed between the gene expression and tumor grade and type, with the highest expression being noted for medulloblastomas, followed by ependymomas, and the lowest for pilocytic astrocytomas. Most members of miR-17-92, miR-106a-363 and miR-106b-25 clusters were upregulated and the highest expression was noted for miR-18a and miR-18b. The rest of the miRNAs, including miR-19a, miR-92a, miR-106a, miR-93, or miR-25 also showed high values. miR-17-5p, miR-20a obtained a high level of expression in medulloblastomas and ependymomas, while close to the control in the pilocytic astrocytoma samples. miRNA expression also depended on tumor grade and histology.
Keywords: OncomiR-1; brain tumor; ependymoma; medulloblastoma; miR-106a-363; miR-106b-25; miR-17-92; microRNA; pilocytic astrocytoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of miRNA-target genes network in pediatric brain tumors.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17922. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68945-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095557 Free PMC article.
-
miR-106a-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration of astrocytoma cells and promotes apoptosis by targeting FASTK.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e72390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072390. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24013584 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA regulation of a cancer network: consequences of the feedback loops involving miR-17-92, E2F, and Myc.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 16;105(50):19678-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811166106. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19066217 Free PMC article.
-
Good or not good: Role of miR-18a in cancer biology.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020 Sep-Oct;25(5):808-819. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.07.006. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020. PMID: 32884453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oncogenic Relevance of miR-17-92 Cluster and Its Paralogous miR-106b-25 and miR-106a-363 Clusters in Brain Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 16;19(3):879. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030879. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29547527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of miRNA-target genes network in pediatric brain tumors.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17922. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68945-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095557 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs as major players in brain health and disease: current knowledge and future perspectives.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jan 13;11(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02283-x. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 39805813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HHOMR: a hybrid high-order moment residual model for miRNA-disease association prediction.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jul 25;25(5):bbae412. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae412. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39175132 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA dynamic expression regulates invariant NKT cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Aug;78(16):6003-6015. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03895-7. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34236444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the Cell Cycle by ncRNAs Affects the Efficiency of CDK4/6 Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 18;24(10):8939. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108939. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Visani M., de Biase D., Marucci G., Cerasoli S., Nigrisoli E., Bacchi Reggiani M.L., Albani F., Baruzzi A., Pession A. Expression of 19 microRNAs in glioblastoma and comparison with other brain neoplasia of grades I-III. Mol. Oncol. 2014;8:417–430. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.12.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

