Epigenetic Modifications Induced by Olive Oil and Its Phenolic Compounds: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33430487
- PMCID: PMC7826507
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26020273
Epigenetic Modifications Induced by Olive Oil and Its Phenolic Compounds: A Systematic Review
Abstract
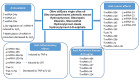
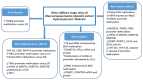
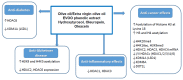
Many studies demonstrated that olive oil (especially extra virgin olive oil: EVOO) phenolic compounds are bioactive molecules with anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging and neuroprotective activities. These effects have been recently attributed to the ability of these compounds to induce epigenetics modifications such as miRNAs expression, DNA methylation and histone modifications. In this study, we systematically review and discuss, following the PRISMA statements, the epigenetic modifications induced by EVOO and its phenols in different experimental systems. At the end of literature search through "PubMed", "Web of Science" and "Scopus", 43 studies were selected.Among them, 22 studies reported data on miRNAs, 15 on DNA methylation and 13 on histone modification. Most of the "epigenomic" changes observed in response to olive oil phenols' exposure were mechanistically associated with the cancer preventive and anti-inflammatory effects. In many cases, the epigenetics effects regarding the DNA methylation were demonstrated for olive oil but without any indication regarding the presence or not of phenols. Overall, the findings of the present systematic review may have important implications for understanding the epigenetic mechanisms behind the health effects of olive oil. However, generally no direct evidence was provided for the causal relationships between epigenetics modification and EVOO health related effects. Further studies are necessary to demonstrate the real physiological consequences of the epigenetics modification induced by EVOO and its phenolic compounds.
Keywords: DNA methylation; anti-cancer; anti-inflammatory; epigenetics; extra virgin olive oil; histone modification; miRNA; phenolic compounds; secoiridoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Soltani S., Jayedi A., Shab-Bidar S., Becerra-Tomás N., Salas-Salvadó J. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet in relation to all-cause mortality: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Adv. Nutr. 2019;10:1029–1039. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmz041. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

